Wi-Fi R-MESH

Wi-Fi R-MESH
Overview

Wi-Fi R-Mesh is an innovative tree-topology mesh network architecture designed to extend Wi-Fi coverage. Through multi-level node collaboration, it effectively eliminates signal dead zones in traditional networks, enabling devices far from the AP to enjoy stable, high-speed connectivity.
As shown in the figure, the network supports multiple root nodes for broader coverage. Root nodes STA1 and STA2 extend to multi-level child nodes (STA1-0 to STA1-3 and STA2-0 to STA2-3), forming a clearly layered tree structure.
This technology is ideal for large-area scenarios such as villas and multi-story office buildings, using multi-hop relaying to achieve seamless signal extension and eliminate coverage blind spots.
Efficient Forwarding
Traditional mesh networks require relay nodes to enable a hotspot (SoftAP) and rely on higher-layer NAT protocols to assist with forwarding.

In contrast, Wi-Fi R-Mesh, leveraging its innovative technology, implements data forwarding directly at the Wi-Fi driver layer, bypassing the complex processing of traditional TCP/IP protocol stacks, and significantly simplifying the Wi-Fi driver layer (unlike conventional MESH where intermediate nodes need to create hotspots and establish Wi-Fi connections). This design greatly reduces resource consumption of SRAM memory and MCU computing power.
As shown in the figure, data communication between end devices is transparent to R-MESH forwarding. Intermediate relay nodes perform low-level forwarding between nodes via the Wi-Fi MAC layer.

Loop Avoidance
In traditional mesh networks, topology changes can easily create loops. As shown in the figure, when STA1 loses power, STA3 may reconnect to STA4 as a new upstream node, resulting in a loop among STA3-STA4-STA5. Packets within this loop will be repeatedly forwarded between nodes, failing to reach the AP correctly and causing network congestion.

Wi-Fi R-Mesh nodes keep track of their descendant information and proactively avoid selecting any descendant as their upstream node, thereby preventing loops.

No Routing Management
Traditional mesh networks typically require maintaining a routing table in the upper-layer software at each node, and the software consults this table during packet forwarding to determine the next hop.

R-Mesh, by contrast, records routing information—such as father and child nodes—directly in each node's registers and employs dedicated circuitry to identify and forward packets that need relaying, thereby eliminating the overhead of software-based routing table maintenance and lookup.

Low RTT
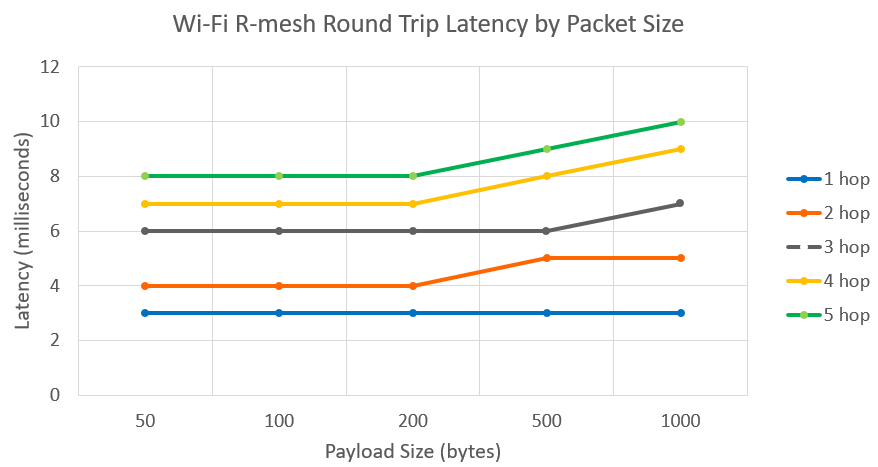
The minimalist architecture of Wi-Fi R-Mesh significantly enhances real-time performance. Even across multiple hops, it maintains high throughput and extremely low latency, making it particularly suitable for IoT and smart-home scenarios that demand low power and high efficiency.
As shown in the figure, as packet size increases, round-trip latency across different hop counts (from 1 to 5 hops) grows very slowly. Even with 5-hop transmission (green curve), the latency is significantly lower than that in traditional Mesh networks.
PC Development Tool
Basic functionality
Gravitation is an open-source R-Mesh visualization testing tool that runs on PC and provides the following basic features.
- Visualize the network at a macro level: present all node connections in a tree diagram
- Inspect node-level details: display each node's IP address, MAC address, last online time, and other basic information
- Monitor link quality: calculate a score based on Wi-Fi signal strength to assess the quality of links between the node and the AP
- Survey neighboring peers: check whether other R-Mesh nodes exist around a given node
- Remote firmware updates: batch transfer new firmware versions to nodes via Wi-Fi for updating
- Latency and packet loss testing: run ping tests with each node to gather average RTT and packet loss statistics
Simulation Testing
Gravitation can send debugging commands to each node via the serial port to adjust the signal strength between nodes, thereby simulating different testing distances.
Users can use this feature to simulate network conditions under various scenarios. Below are several typical cases:
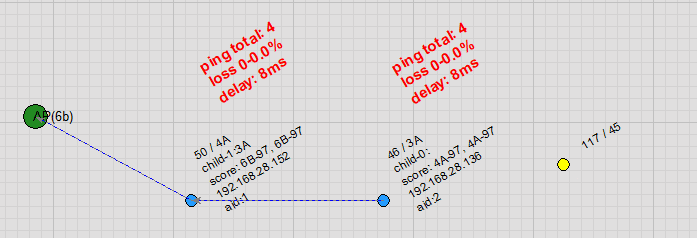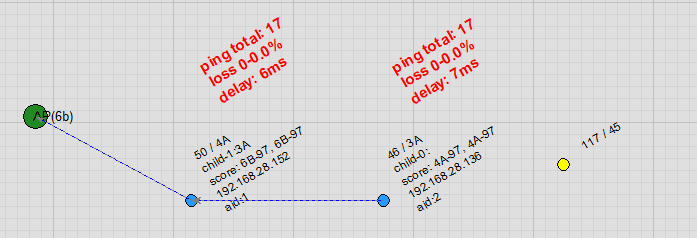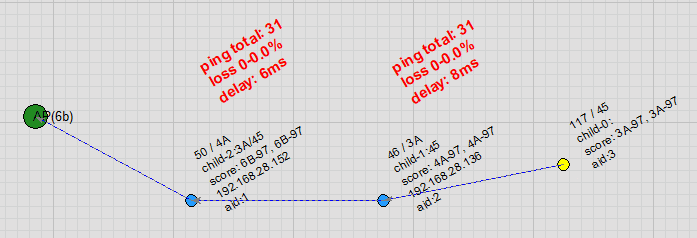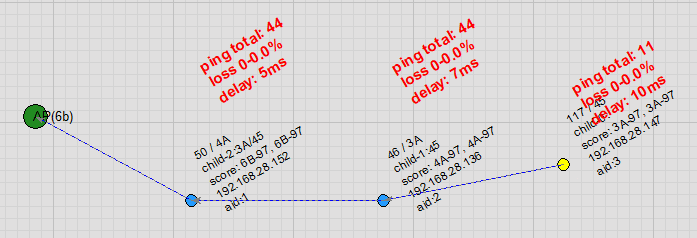
Remote node connection: Nodes that are far from the AP and cannot detect the AP’s beacon will rely on nearby R‑Mesh nodes to help complete the connection.
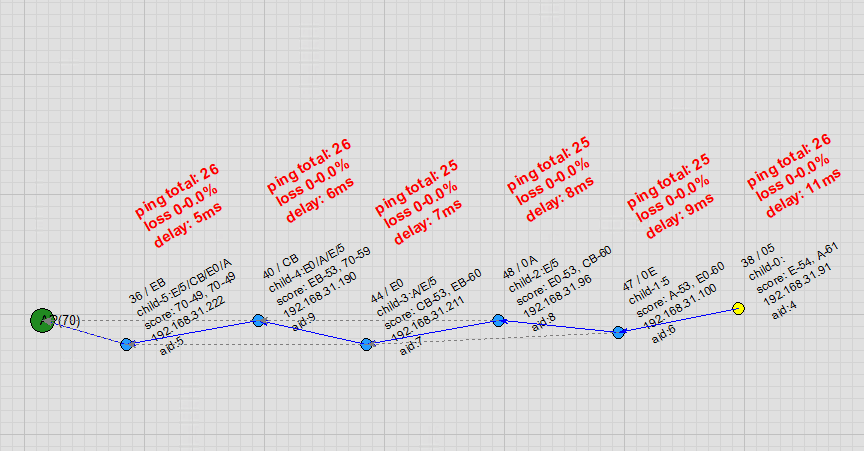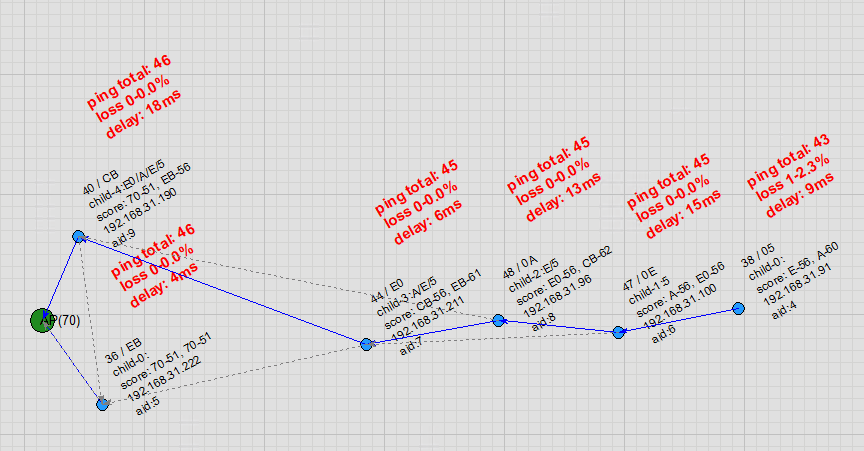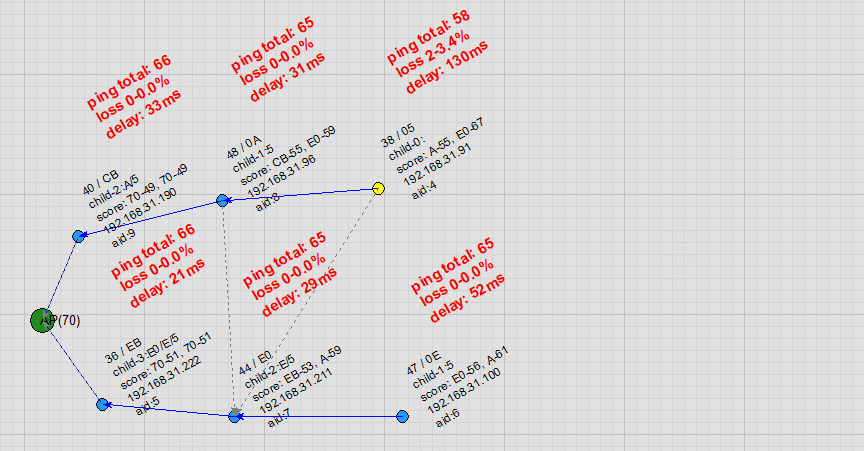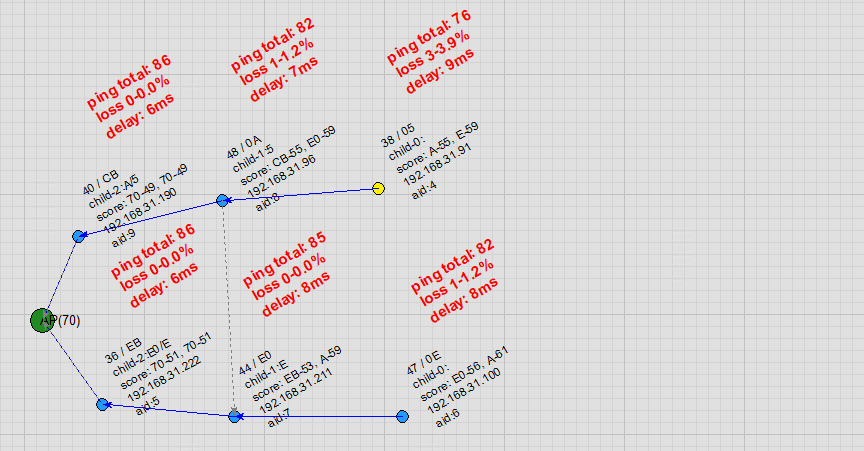
Node Free Drag: Users can drag nodes on the topology map. As a node moves, it automatically detects and switches to a more suitable parent node, with virtually no packet loss in ping during the handover.
Parent Node Disconnection: When a parent node goes offline, the child node quickly switches to a candidate parent node, bringing along its own child nodes. Once the original parent node recovers, the child node switches back together with its child nodes. Throughout these transitions, ping shows virtually no packet loss.
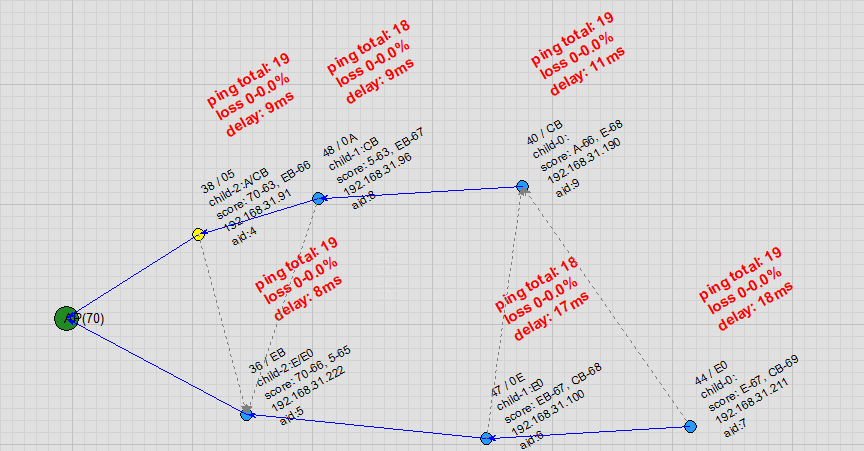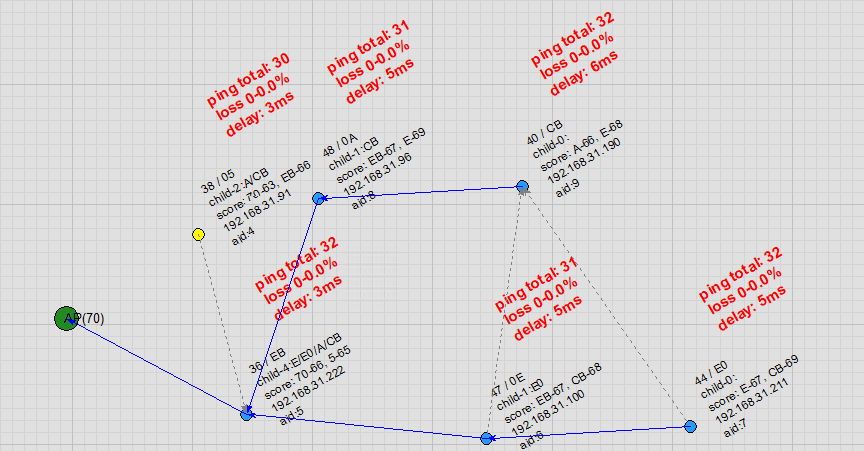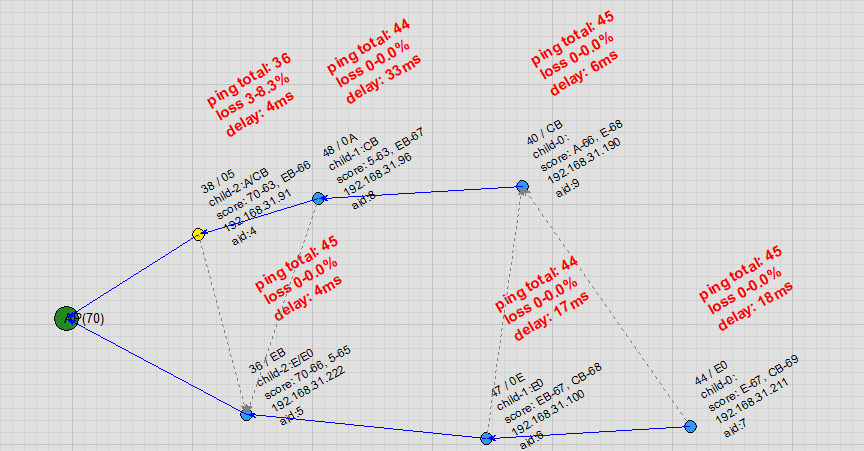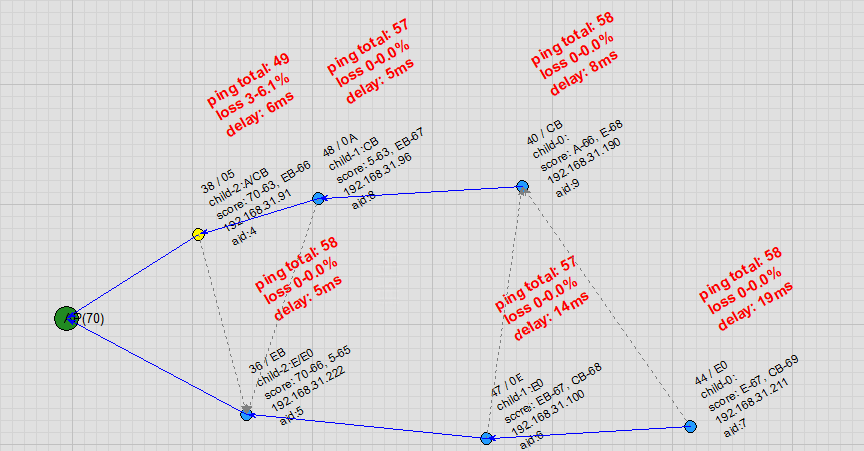
AP Channel Switch: When the AP leaves its original channel, all nodes disconnect. After the AP starts on the new channel, the R-Mesh network is quickly reconstructed.
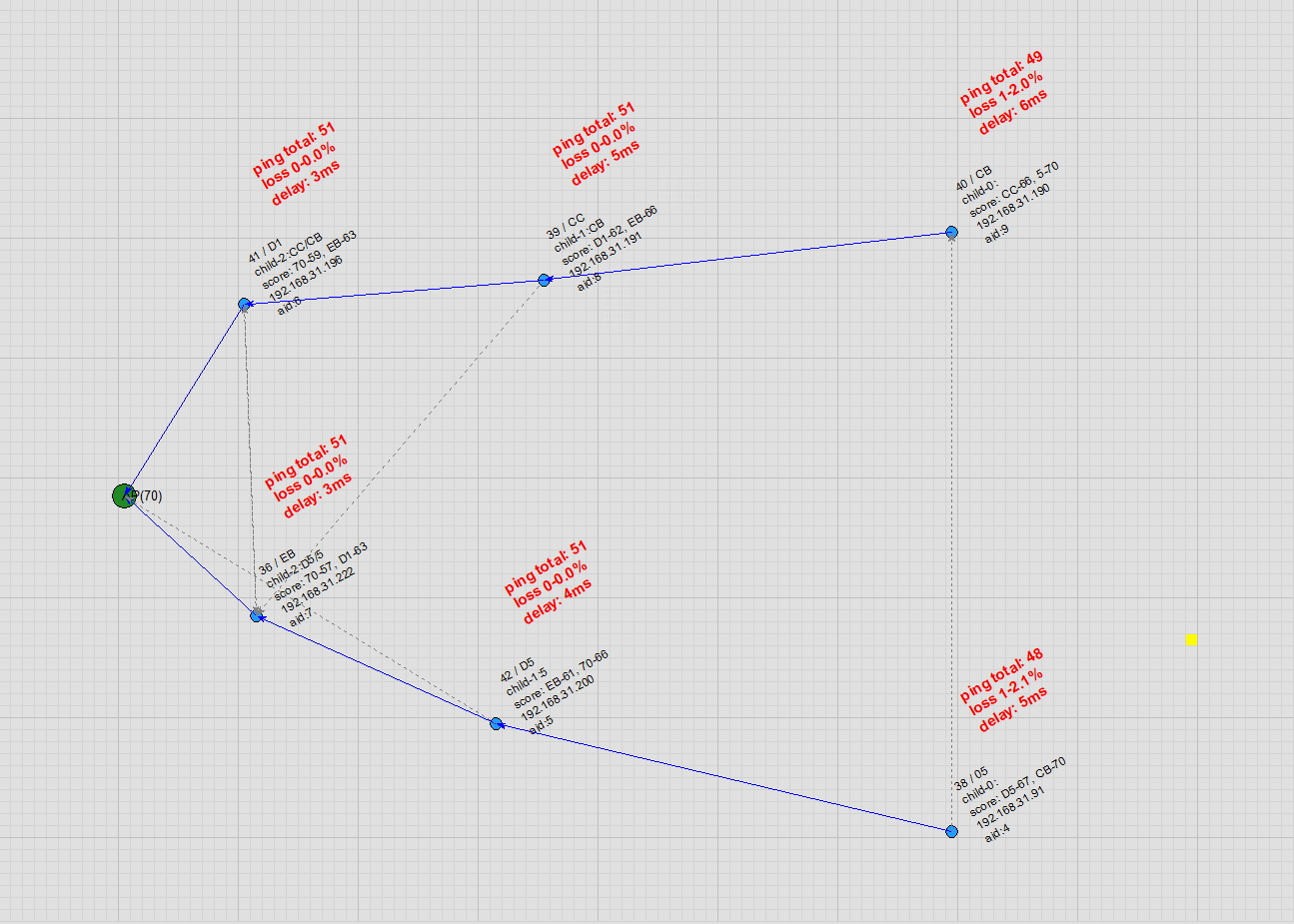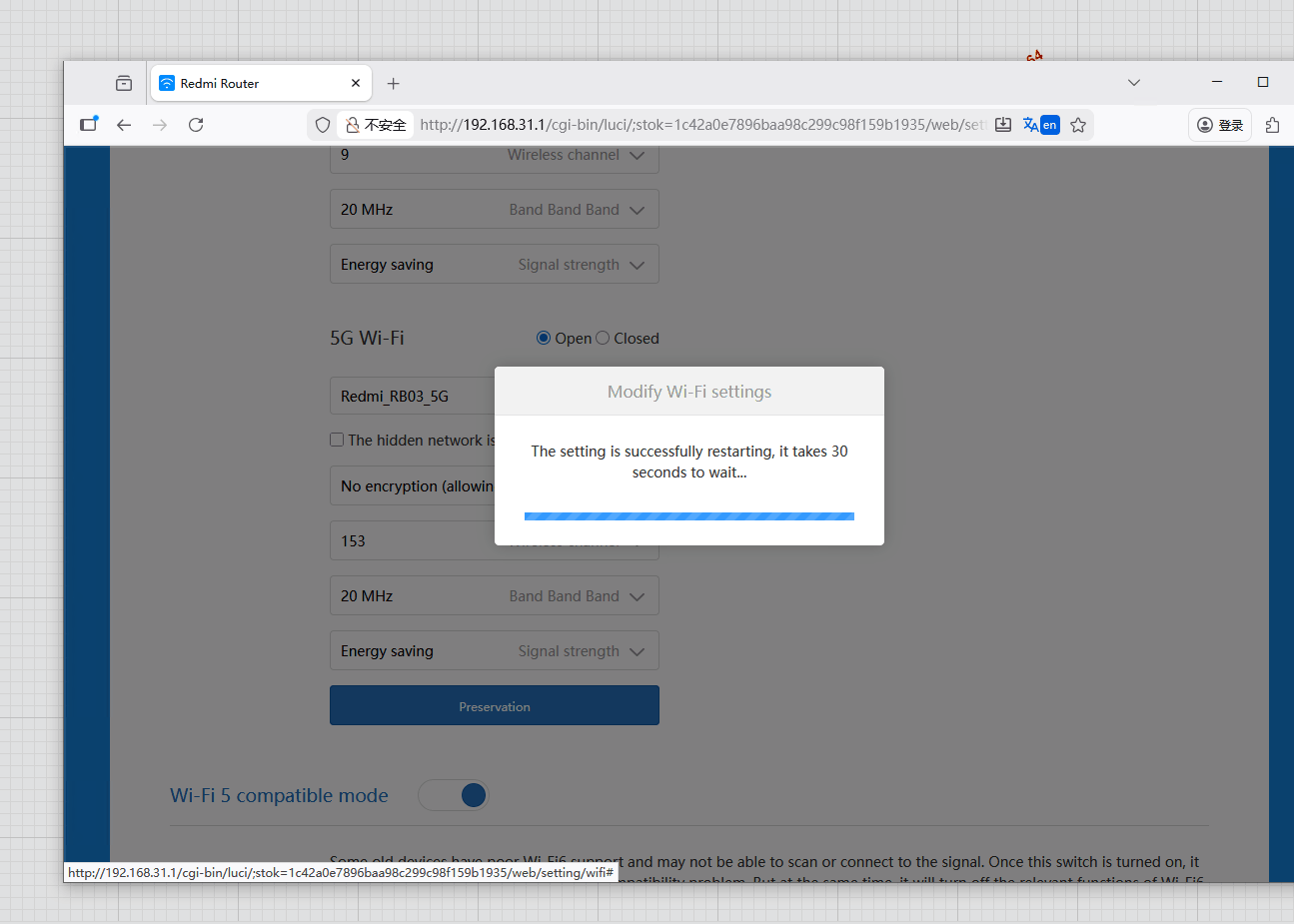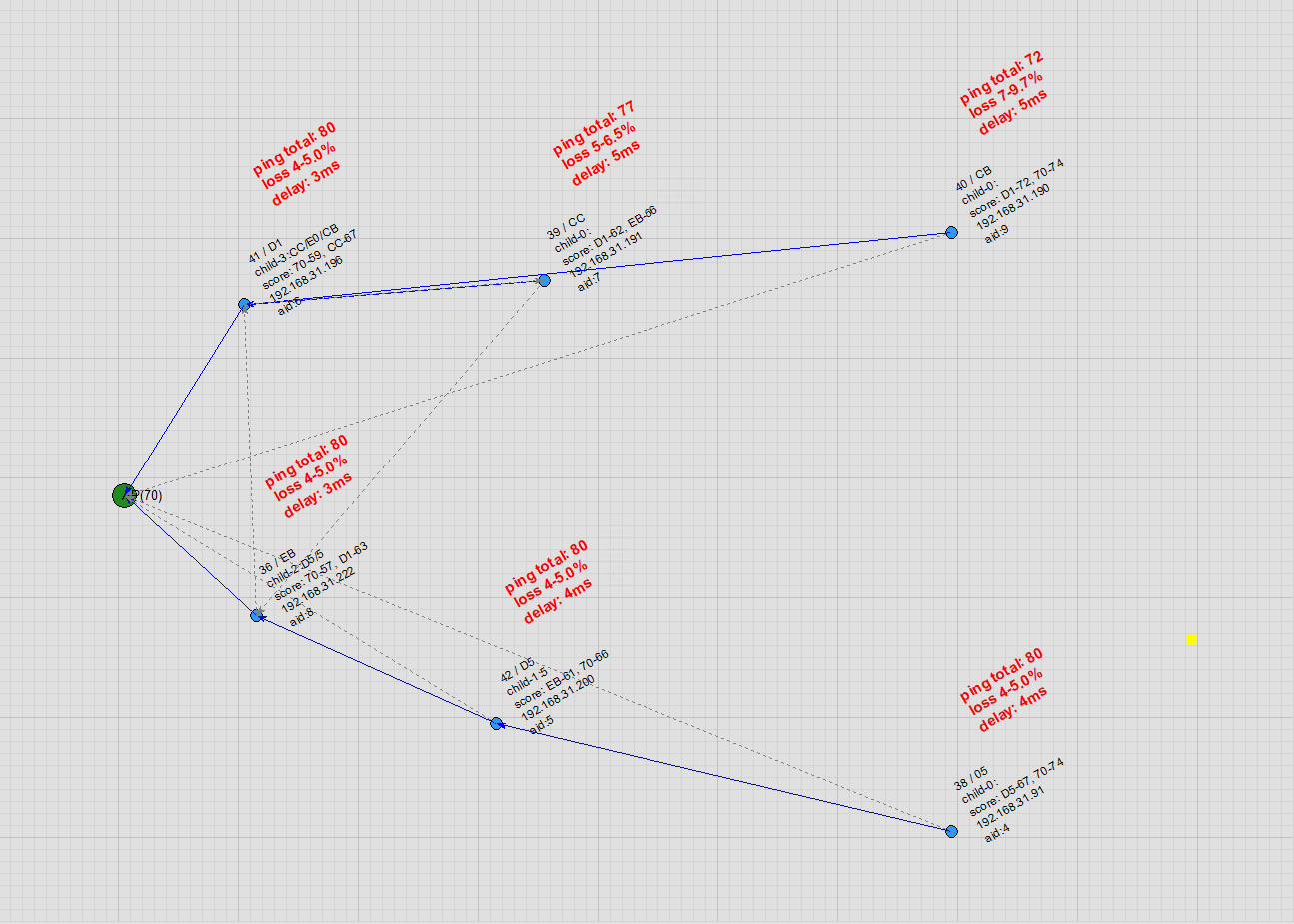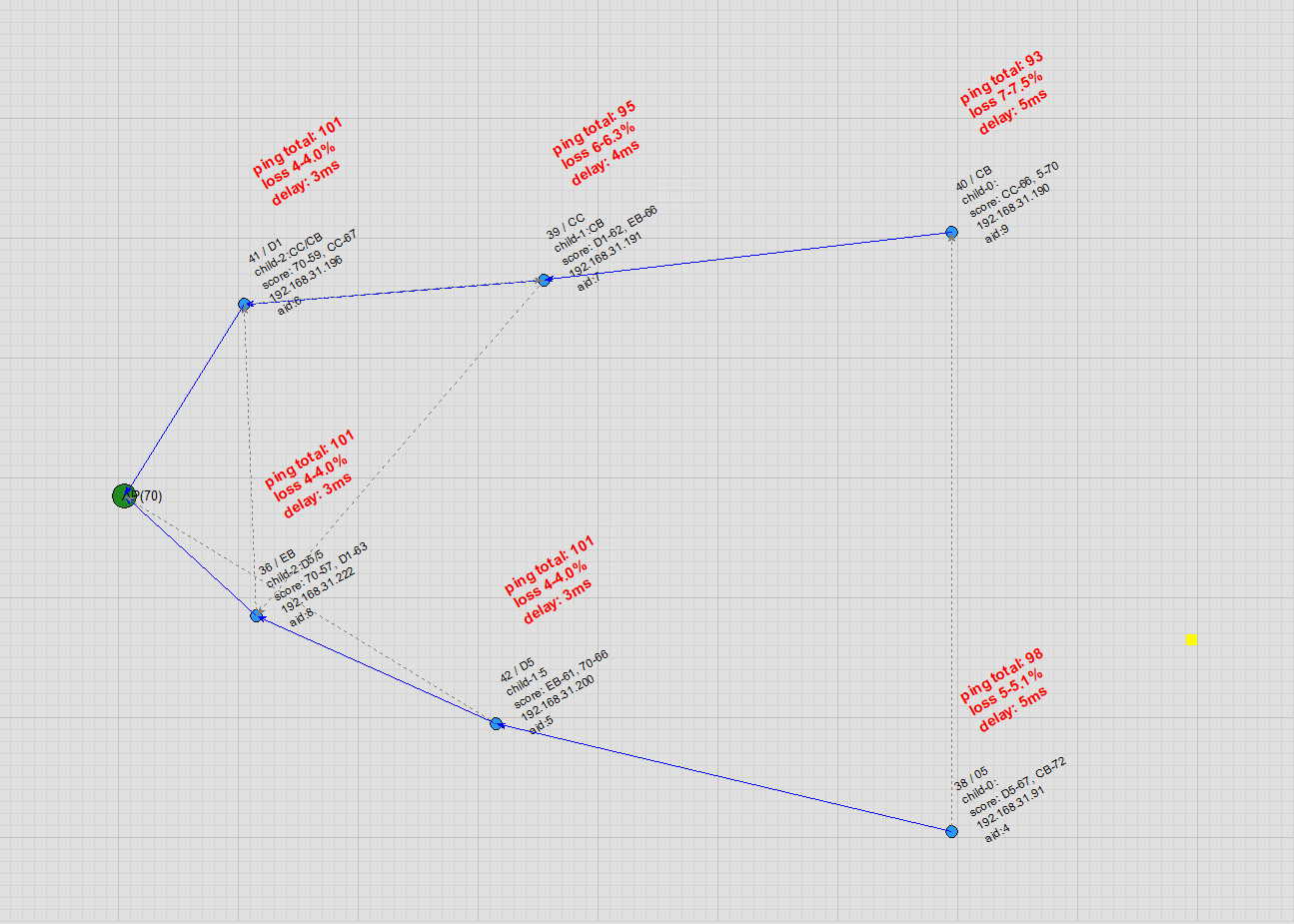
Node Auto Movement: Users can enable automatic node movement on the topology map. During movement, the node automatically detects and switches to a more suitable parent node, with virtually no packet loss in ping during the handover.

Mobile Development Tool
MGravitation is an open-source R-Mesh visualization testing tool that runs on mobile devices and provides the following features:
- Visualize the network at a macro level: present all node connections in a tree diagram
- Inspect node-level details: display each node's IP address, MAC address, last online time, and other basic information
- Monitor link quality: calculate a score based on Wi-Fi signal strength to assess the quality of links between the node and the AP
- Survey neighboring peers: check whether other R-Mesh nodes exist around a given node
- Remote firmware updates: batch transfer new firmware versions to nodes via Wi-Fi for updating
- Assist with bulk provisioning: Powered by the R-Mesh Provisioning Protocol (RPP), it enables one-click Wi-Fi provisioning for a large number of nodes

R-Mesh Provisioning Protocol
The R-Mesh Provisioning Protocol is designed to improve network deployment efficiency in scenarios with a large number of R-Mesh nodes.
Users can first use the mobile app to deliver Wi-Fi credentials to one R-Mesh node via Bluetooth. Once this node successfully connects to Wi-Fi, the remaining nodes will automatically join the network following the R-Mesh Zero Provisioning Protocol (ZRPP), enabling rapid onboarding of large-scale nodes.

Advantages
All Mesh protocols are implemented at the Wi-Fi driver layer. Regardless of whether it's a root node or a child node, the application layer can view the current node as a Wi-Fi Station connected to an AP.
Child nodes can quickly switch parent nodes, and the switching process does not affect data communication. A node can carry all of its child nodes to switch to another parent node together, without affecting the data communication of any nodes.

R-Mesh data forwarding is efficiently completed in the underlying driver, with extremely short software processing time. Even devices that go through multiple hops maintain relatively high throughput.

There's no need for algorithms to maintain routing tables, making the entire network very stable. Traditional problems like routing loops in Mesh networks do not occur.
Typical Applications
- Smart Lighting: Automatically network lights to operate without a central gateway, enabling whole-house intelligent lighting control.
- Smart Agriculture: Automatically network devices like soil temperature/humidity sensors and pest-monitoring cameras to overcome complex terrain limitations in farmland. Achieves synchronous data collection across expansive farmland and coordinated smart irrigation control.
- PV Micro-inverters: Automatically network micro-inverter devices to effectively resolve signal coverage challenges in complex building environments. Enables real-time monitoring and remote control of distributed photovoltaic units.
Development Resources
 |
SDK Download | Link |
 |
R-MESH Trial Firmware Download | Link |
 |
R-MESH Development Guide | Link |
 |
R-MESH Video Introduction | Link |
 |
R-MESH PC Development Tool Source Code | Link |
 |
R-MESH Mobile Development Tool Source Code | Link |
 |
Contact Us | Link |
Recommended ICs
| Features | Filter | RTL8721Dx | RTL8720E | RTL8710E | RTL8726E | RTL8713E | RTL8730E | RTL8721F | RTL872xD | RTL8735B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Processor |
Cortex-M | Cortex-M | Cortex-M | Cortex-M | Cortex-M | Cortex-A | Cortex-M | Cortex-M | Cortex-M | |
| DSP | ||||||||||
| ISP | ||||||||||
| Arm TrustZone | ||||||||||
| Dual Band | ||||||||||
| Wi-Fi 6 | ||||||||||
| R-MESH | ||||||||||
| Ultra-low Power | ||||||||||
| Ethernet | ||||||||||
| BT Dual Mode | ||||||||||
| HMI | ||||||||||
| Audio ADC | ||||||||||
| Audio DAC | ||||||||||
| SDIO Host | ||||||||||
| SD/EMMC Host | ||||||||||
| USB | ||||||||||
|
BT Dedicated Antenna |
||||||||||
| A2C |
