AIVoice Development Guide
Supported ICs
Overview
AIVoice is an offline AI solution developed by Realtek, including local algorithm modules like Audio Front End (Signal Processing), Keyword Spotting, Voice Activity Detection, Speech Recognition etc. It can be used to build smart voice related applications on Realtek Ameba SoCs.
AIVoice can be used as a purely offline solution on its own, or it can be combined with cloud systems such as voice recognition, LLMs to create a hybrid online and offline voice interaction solution.
Applications
Application solutions
Pure Offline: Standalone AIVoice usage supporting local wake-up, recognition, and other functions.
Offline-Online Hybrid: AIVoice integrated with cloud-based systems (e.g., speech recognition, LLM) for local wake-up followed by cloud interaction.
Application products
Smart Home: Smart speakers like Amazon Echo and Google Nest, or smart home appliances. Control lighting, temperature, and other smart devices through voice commands.
Smart Toys: AI story machines, educational robots, companion robots etc. These toys can engage in natural conversations with users, answering questions, telling stories, or providing bilingual education.
In-Car Systems: Enable drivers to navigate, make calls, and play music using voice commands, ensuring driving safety and improving the driving experience.
Wearable Products: Smartwatches, smart headphones, and health monitoring devices etc. User can use voice control to check and send messages, control music player, answer calls etc.
Meeting Scenarios: Transcribe meeting content in real-time, helping participants better record and review discussion points.
Modules
Modules |
Functions |
|---|---|
Enhancing speech signals and reducing noise, including submodules: AEC, Beamforming, NS, AGC, SSL |
|
Detecting specific wakeup words to trigger voice assistants, such as |
|
Detecting speech segments or noise segments |
|
Detecting offline voice control commands |
Flows
Some algorithm flows have been implemented to facilitate user development.
AFE+KWS+ASR (full_flow): A full flow including local algorithm modules: AFE, KWS and ASR. AFE and KWS are always-on, ASR turns on and supports continuous recognition when KWS detects the keyword. ASR exits after timeout.
AFE+KWS: Flow including AFE and KWS, always-on.
AFE+KWS+VAD: Flow including AFE, KWS and VAD. AFE and KWS are always-on, VAD turns on and supports continuous activity detention when KWS detects the keyword. VAD exits after timeout.
If alternative module combinations (e.g. AFE+VAD) or exclusion of specific AIVoice components is required, custom workflows can be implemented by using individual module interfaces through dedicated API calls.
Repository and Dependencies
Code Repository
AIVoice source code is hosted on GitHub: ameba-aivoice.
SDK Dependencies
AIVoice requires one of the following SDKs:
SDK selection depends on the SoC and OS:
SoC |
OS |
SDK |
AIVoice Path |
|---|---|---|---|
RTL8721Dx/RTL8730E |
FreeRTOS |
ameba-rtos |
{SDK}/component/aivoice |
RTL8713E/RTL8726E |
FreeRTOS |
ameba-dsp |
{SDK}/lib/aivoice |
RTL8730E |
Linux |
ameba-linux |
{SDK}/apps/aivoice |
Download Methods
Auto Download (Recommended): Follow the extended XDK download method in SDK Download
Manual Download: Clone the following sub-repositories separately and place them in the specified path of the base SDK (see SDK Download )
Component |
Github repo |
SDK path |
|---|---|---|
tflite_micro |
{SDK}/component/tflite_micro |
|
aivoice |
{SDK}/component/aivoice |
Download ameba-dsp (for building DSP image)
Auto download (Recommended): Use the following command to download ameba-dsp along with its submodules:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/Ameba-AIoT/ameba-dsp
Manual download: Clone the following sub-repositories separately and place them in the specified path under ameba-dsp.
Component |
Github repo |
SDK path |
|---|---|---|
tflite_micro |
{SDK}/lib/tflite_micro |
|
aivoice |
{SDK}/lib/aivoice |
Download ameba-rtos (for building KM4 & KR4 image)
Auto Download (Recommended): Follow the extended XDK download method in SDK Download
Manual Download: Clone ameba-aivoice separately and place it under
{SDK}/component/aivoiceof the base SDK (see SDK Download )
Download ameba-dsp (for building DSP image)
Auto download (Recommended): Use the following command to download ameba-dsp along with its submodules:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/Ameba-AIoT/ameba-dsp
Manual download: Clone the following sub-repositories separately and place them in the specified path under ameba-dsp.
Component |
Github repo |
SDK path |
|---|---|---|
tflite_micro |
{SDK}/lib/tflite_micro |
|
aivoice |
{SDK}/lib/aivoice |
Download ameba-rtos (for building KM4 & KR4 image)
Auto Download (Recommended): Follow the extended XDK download method in SDK Download
Manual Download: Clone ameba-aivoice separately and place it under
{SDK}/component/aivoiceof the base SDK (see SDK Download )
Auto Download (Recommended): Follow the extended XDK download method in SDK Download
Manual Download: Clone the following sub-repositories separately and place them in the specified path of the base SDK (see SDK Download )
Component |
Github repo |
SDK path |
|---|---|---|
tflite_micro |
{SDK}/component/tflite_micro |
|
aivoice |
{SDK}/component/aivoice |
Download the Linux SDK: Refer to SDK Download .
Download AIVoice: Clone the ameba-aivoice repository separately and place it under
{SDK}/apps/aivoice.
File Description
The AIVoice repository directory structure is as follows. Algorithm and model resources are provided as prebuilt libraries under prebuilts/lib/ameba_rtos/rtl8721dx_km4:
├── examples
│ ├── build_utils Tools and configuration files for building examples
│ ├── full_flow_offline Example 1: AIVoice offline (using pre-recorded audio)
│ └── speechmind_demo Example 2: SpeechMind real-time demo (using microphone input)
├── include
│ ├── aivoice_afe_config.h AFE configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_asr_config.h ASR configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_interface.h AIVoice interface header file
│ ├── aivoice_kws_config.h KWS configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_sdk_config.h Common configuration header file
│ └── aivoice_vad_config.h VAD configuration header file
├── prebuilts
│ ├── bin Binary resources
│ ├── image Prebuilt images
│ │ └── ameba_dsp
│ └── lib Prebuilt libraries
│ ├── ameba_dsp RTL8713E/RTL8726E libraries
│ ├── ameba_linux RTL8730E libraries (Linux)
│ └── ameba_rtos
│ ├── rtl8721dx_km4 RTL8721Dx libraries
│ └── rtl8730e_ca32_freertos RTL8730E libraries (RTOS)
└── tools
└── pack_resources Binary resource pack tool
Additionally, the
TensorFlowLite-Micro
dependency for AIVoice is not provided as a prebuilt library. Enable TFLITE MICRO in menuconfig when building images.
The AIVoice repository directory structure is as follows:
├── examples
│ ├── build_utils Tools and configuration files for building examples
│ ├── full_flow_offline Example 1: AIVoice offline (using pre-recorded audio)
│ └── speechmind_demo Example 2: SpeechMind real-time demo (using microphone input)
├── include
│ ├── aivoice_afe_config.h AFE configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_asr_config.h ASR configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_interface.h AIVoice interface header file
│ ├── aivoice_kws_config.h KWS configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_sdk_config.h Common configuration header file
│ └── aivoice_vad_config.h VAD configuration header file
├── prebuilts
│ ├── bin Binary resources
│ ├── image Prebuilt images
│ │ └── ameba_dsp
│ └── lib Prebuilt libraries
│ ├── ameba_dsp RTL8713E/RTL8726E libraries
│ ├── ameba_linux RTL8730E libraries (Linux)
│ └── ameba_rtos
│ ├── rtl8721dx_km4 RTL8721Dx libraries
│ └── rtl8730e_ca32_freertos RTL8730E libraries (RTOS)
└── tools
└── pack_resources Binary resource pack tool
Algorithm resources (models, AFE parameters, FST etc.) are provided in both library and binary formats to accommodate different development needs:
Format |
Library |
Binary File |
|---|---|---|
Resource Path |
prebuilts/lib/ameba_dsp |
prebuilts/bin |
Prebuilt Image Path |
N/A |
prebuilts/image/ameba_dsp |
Required SDK |
ameba-rtos + ameba-dsp |
ameba-rtos |
Image Composition |
km4_boot_all.bin kr4_km4_app.bin dsp_all.bin |
km4_boot_all.bin kr4_km4_app.bin aivoice_models.bin dsp_all.bin |
Resource Switching Method |
Replace linked library files in ameba-dsp and recompile the DSP project |
Select version via menuconfig in ameba-rtos and repack aivoice_models.bin |
Skill Requirement |
DSP development expertise required |
No DSP development needed |
Flexibility |
High (custom DSP logic supported) |
Low (uses prebuilt DSP image) |
Use Case |
Custom DSP requirements |
Rapid integration, avoiding DSP development |
The AIVoice repository directory structure is as follows:
├── examples
│ ├── build_utils Tools and configuration files for building examples
│ ├── full_flow_offline Example 1: AIVoice offline (using pre-recorded audio)
│ └── speechmind_demo Example 2: SpeechMind real-time demo (using microphone input)
├── include
│ ├── aivoice_afe_config.h AFE configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_asr_config.h ASR configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_interface.h AIVoice interface header file
│ ├── aivoice_kws_config.h KWS configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_sdk_config.h Common configuration header file
│ └── aivoice_vad_config.h VAD configuration header file
├── prebuilts
│ ├── bin Binary resources
│ ├── image Prebuilt images
│ │ └── ameba_dsp
│ └── lib Prebuilt libraries
│ ├── ameba_dsp RTL8713E/RTL8726E libraries
│ ├── ameba_linux RTL8730E libraries (Linux)
│ └── ameba_rtos
│ ├── rtl8721dx_km4 RTL8721Dx libraries
│ └── rtl8730e_ca32_freertos RTL8730E libraries (RTOS)
└── tools
└── pack_resources Binary resource pack tool
Algorithm resources (models, AFE parameters, FST etc.) are provided in both library and binary formats to accommodate different development needs:
Format |
Library |
Binary File |
|---|---|---|
Resource Path |
prebuilts/lib/ameba_dsp |
prebuilts/bin |
Prebuilt Image Path |
N/A |
prebuilts/image/ameba_dsp |
Required SDK |
ameba-rtos + ameba-dsp |
ameba-rtos |
Image Composition |
km4_boot_all.bin kr4_km4_app.bin dsp_all.bin |
km4_boot_all.bin kr4_km4_app.bin aivoice_models.bin dsp_all.bin |
Resource Switching Method |
Replace linked library files in ameba-dsp and recompile the DSP project |
Select version via menuconfig in ameba-rtos and repack aivoice_models.bin |
Skill Requirement |
DSP development expertise required |
No DSP development needed |
Flexibility |
High (custom DSP logic supported) |
Low (uses prebuilt DSP image) |
Use Case |
Custom DSP requirements |
Rapid integration, avoiding DSP development |
The AIVoice repository directory structure is as follows. Algorithm and model resources are provided as prebuilt libraries under prebuilts/lib/ameba_rtos/rtl8730e_ca32_freertos:
├── examples
│ ├── build_utils Tools and configuration files for building examples
│ ├── full_flow_offline Example 1: AIVoice offline (using pre-recorded audio)
│ └── speechmind_demo Example 2: SpeechMind real-time demo (using microphone input)
├── include
│ ├── aivoice_afe_config.h AFE configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_asr_config.h ASR configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_interface.h AIVoice interface header file
│ ├── aivoice_kws_config.h KWS configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_sdk_config.h Common configuration header file
│ └── aivoice_vad_config.h VAD configuration header file
├── prebuilts
│ ├── bin Binary resources
│ ├── image Prebuilt images
│ │ └── ameba_dsp
│ └── lib Prebuilt libraries
│ ├── ameba_dsp RTL8713E/RTL8726E libraries
│ ├── ameba_linux RTL8730E libraries (Linux)
│ └── ameba_rtos
│ ├── rtl8721dx_km4 RTL8721Dx libraries
│ └── rtl8730e_ca32_freertos RTL8730E libraries (RTOS)
└── tools
└── pack_resources Binary resource pack tool
Additionally, the
TensorFlowLite-Micro
dependency for AIVoice is not provided as a prebuilt library. Enable TFLITE MICRO in the project configuration when building images.
The AIVoice repository directory structure is as follows. TensorFlowLite, algorithm, and models are provided as prebuilt libraries under prebuilts/lib/ameba_linux:
├── examples
│ ├── build_utils Tools and configuration files for building examples
│ ├── full_flow_offline Example 1: AIVoice offline (using pre-recorded audio)
│ └── speechmind_demo Example 2: SpeechMind real-time demo (using microphone input)
├── include
│ ├── aivoice_afe_config.h AFE configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_asr_config.h ASR configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_interface.h AIVoice interface header file
│ ├── aivoice_kws_config.h KWS configuration header file
│ ├── aivoice_sdk_config.h Common configuration header file
│ └── aivoice_vad_config.h VAD configuration header file
├── prebuilts
│ ├── bin Binary resources
│ ├── image Prebuilt images
│ │ └── ameba_dsp
│ └── lib Prebuilt libraries
│ ├── ameba_dsp RTL8713E/RTL8726E libraries
│ ├── ameba_linux RTL8730E libraries (Linux)
│ └── ameba_rtos
│ ├── rtl8721dx_km4 RTL8721Dx libraries
│ └── rtl8730e_ca32_freertos RTL8730E libraries (RTOS)
└── tools
└── pack_resources Binary resource pack tool
Note
examples/speechmind_demo contains only the DSP part for RTL8713E/RTL8726E. For example 2’s codes of MCU part (RTL8713E/RTL8726E) or other SOCs, refer to speechmind.
Interface
Module Interfaces
Interface |
Module |
|---|---|
aivoice_iface_afe_v1 |
AFE |
aivoice_iface_vad_v1 |
VAD |
aivoice_iface_kws_v1 |
KWS |
aivoice_iface_asr_v1 |
ASR |
All interfaces support below functions:
create()
destroy()
reset()
feed()
Please refer to ${aivoice_lib_dir}/include/aivoice_interface.h for details.
Flow Interfaces
Interface |
Flow |
|---|---|
aivoice_iface_full_flow_v1 |
AFE+KWS+ASR |
aivoice_iface_afe_kws_v1 |
AFE+KWS |
aivoice_iface_afe_kws_vad_v1 |
AFE+KWS+VAD |
All interfaces support below functions:
create()
destroy()
reset()
feed()
Please refer to ${aivoice_lib_dir}/include/aivoice_interface.h for details.
Event and Callback Message
aivoice_out_event_type |
Event trigger time |
Callback message |
|---|---|---|
AIVOICE_EVOUT_VAD |
When VAD detects start or end point of a speech segment |
Struct includes VAD status, offset. |
AIVOICE_EVOUT_WAKEUP |
When KWS detects keyword |
JSON string includes ID, keyword, and score. Example: {“id”:2,”keyword”:”ni-hao-xiao-qiang”,”score”:0.9} |
AIVOICE_EVOUT_ASR_RESULT |
When ASR detects command word |
JSON string includes FST type, commands and ID. Example: {“type”:0,”commands”:[{“rec”:”play music”,”id”:14}]} |
AIVOICE_EVOUT_AFE |
Every frame when AFE got input |
Struct includes AFE output data, channel number, etc. |
AIVOICE_EVOUT_ASR_REC_TIMEOUT |
When ASR/VAD exceed timeout duration |
NULL |
AFE Event Definition
struct aivoice_evout_afe {
int ch_num; /* channel number of output audio signal, default: 1 */
short* data; /* enhanced audio signal samples */
char* out_others_json; /* reserved for other output data, like flags, key: value */
};
VAD Event Definition
struct aivoice_evout_vad {
int status; /* 0: vad is changed from speech to silence,
indicating the end point of a speech segment
1: vad is changed from silence to speech,
indicating the start point of a speech segment */
unsigned int offset_ms; /* time offset relative to reset point. */
};
Common Configurations
AIVoice configurable parameters:
- timeout:
In full flow, ASR exits when no command word detected during this duration. In AFE+KWS+VAD flow, VAD works only within this duration after a keyword detected. For AFE+KWS+VAD flow, timeout=-1 disables internal timeout.
- memory_alloc_mode:
Default mode uses SDK default heap. SRAM mode uses SDK default heap while also allocate space from SRAM for memory critical data. SRAM mode is ONLY available on RTL8713E and RTL8726E DSP now.
Refer to ${aivoice_lib_dir}/include/aivoice_sdk_config.h for details.
For non-common configurations, please refer to algorithm module sections.
Example
AIVoice Integration Basics
This section details the standard steps for using AIVoice, these core operations will be utilized in subsequent sample examples. Read this section first to understand fundamental processing logic.
Select aivoice flow or modules needed.
/* step 1:
* Select the aivoice flow you want to use.
* Refer to the end of aivoice_interface.h to see which flows are supported.
*/
const struct rtk_aivoice_iface *aivoice = &aivoice_iface_full_flow_v1;
Build configuration.
/* step 2:
* Modify the default configure if needed.
* You can modify 0 or more configures of afe/vad/kws/...
*/
struct aivoice_config config;
memset(&config, 0, sizeof(config));
/*
* here we use afe_res_2mic50mm for example.
* you can change these configuratons according the afe resource you used.
* refer to aivoce_afe_config.h for details;
*
* afe_config.mic_array MUST match the afe resource you linked.
*/
struct afe_config afe_param = AFE_CONFIG_ASR_DEFAULT_2MIC50MM; // change this according to the linked afe resource.
config.afe = &afe_param;
/*
* ONLY turn on these settings when you are sure about what you are doing.
* it is recommend to use the default configure,
* if you do not know the meaning of these configure parameters.
*/
struct vad_config vad_param = VAD_CONFIG_DEFAULT();
vad_param.left_margin = 300; // you can change the configure if needed
config.vad = &vad_param; // can be NULL
struct kws_config kws_param = KWS_CONFIG_DEFAULT();
config.kws = &kws_param; // can be NULL
struct asr_config asr_param = ASR_CONFIG_DEFAULT();
config.asr = &asr_param; // can be NULL
struct aivoice_sdk_config aivoice_param = AIVOICE_SDK_CONFIG_DEFAULT();
aivoice_param.timeout = 10;
config.common = &aivoice_param; // can be NULL
Use
create()to create and initialize aivoice instance with given configuration.
/* step 3:
* Create the aivoice instance.
*/
void *handle = aivoice->create(&config);
if (!handle) {
return;
}
Register callback function.
/* step 4:
* Register a callback function.
* You may only receive some of the aivoice_out_event_type in this example,
* depending on the flow you use.
* */
rtk_aivoice_register_callback(handle, aivoice_callback_process, NULL);
The callback function can be modified according to user cases:
static int aivoice_callback_process(void *userdata,
enum aivoice_out_event_type event_type,
const void *msg, int len)
{
(void)userdata;
struct aivoice_evout_vad *vad_out;
struct aivoice_evout_afe *afe_out;
switch (event_type) {
case AIVOICE_EVOUT_VAD:
vad_out = (struct aivoice_evout_vad *)msg;
printf("[user] vad. status = %d, offset = %d\n", vad_out->status, vad_out->offset_ms);
break;
case AIVOICE_EVOUT_WAKEUP:
printf("[user] wakeup. %.*s\n", len, (char *)msg);
break;
case AIVOICE_EVOUT_ASR_RESULT:
printf("[user] asr. %.*s\n", len, (char *)msg);
break;
case AIVOICE_EVOUT_ASR_REC_TIMEOUT:
printf("[user] asr timeout\n");
break;
case AIVOICE_EVOUT_AFE:
afe_out = (struct aivoice_evout_afe *)msg;
// afe will output audio each frame.
// in this example, we only print it once to make log clear
static int afe_out_printed = false;
if (!afe_out_printed) {
afe_out_printed = true;
printf("[user] afe output %d channels raw audio, others: %s\n",
afe_out->ch_num, afe_out->out_others_json ? afe_out->out_others_json : "null");
}
// process afe output raw audio as needed
break;
default:
break;
}
return 0;
}
Use
feed()to input audio data to aivoice.
/* when run on chips, we get online audio stream,
* here we use a fix audio.
* */
const char *audio = (const char *)get_test_wav();
int len = get_test_wav_len();
int audio_offset = 44;
int mics_num = 2;
int afe_frame_bytes = (mics_num + afe_param.ref_num) * afe_param.frame_size * sizeof(short);
while (audio_offset <= len - afe_frame_bytes) {
/* step 5:
* Feed the audio to the aivoice instance.
* */
aivoice->feed(handle,
(char *)audio + audio_offset,
afe_frame_bytes);
audio_offset += afe_frame_bytes;
}
(Optional) Use
reset()if status reset is needed.Use
destroy()to destroy the instance if aivoice is no longer needed.
/* step 6:
* Destroy the aivoice instance */
aivoice->destroy(handle);
Example 1: AIVoice Offline (Using Pre-recorded Audio)
This example shows how to use AIVoice full flow with a pre-recorded 3 channel audio and will run only once after EVB reset. Audio functions such as recording and playback are not integrated.
Example code is under aivoice/examples/full_flow_offline.
Build Example
Enter into SDK directory and run
env.shto set environment variables
cd {SDK}/
source env.sh
Run
ameba.pyto enter the configuration interface
ameba.py menuconfig RTL8721Dx
Navigate through menu path to enable TFLM Library and AIVoice
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG TrustZone --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
GUI Config --->
...
AI Config --->
[*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
Build image
ameba.py build -a full_flow_offline
Add all aivoice example dependencies and linked resources into project
Using lib resources:
cd {DSPSDK}/lib/aivoice/examples/build_utils/ameba_dsp
./add_all_settings_to_project.sh {DSPSDK}/project/project_dsp/ full_flow_offline
Using bin resources:
cd {DSPSDK}/lib/aivoice/examples/build_utils/ameba_dsp
./add_all_settings_to_project.sh {DSPSDK}/project/project_dsp/ full_flow_offline --no_lib_resources
This will insert all the necessary dependencies and linke resources into the project makefile.
Build
dsp_all.bin, output directory{DSPSDK}/source/project/image/.
cd dsp/source/project/auto_build/
./auto_build.sh
Note
The default xtensa configuration is HIFI5_PROD_1123_asic_wUPG, can be modified via configName in {DSPSDK}/source/project/image/dsp_batch.xml.
Refer to MCU project build steps in DSP Build to build the MCU images.
Pack AIVoice Binary Resources
If using AIVoice binary resources, follow these extra steps to prepare aivoice_models.bin:
Enter into SDK directory and run
env.shto set environment variables
cd {SDK}/
source env.sh
Run
ameba.pyto enter the configuration interface
ameba.py menuconfig RTL8713E
Navigate to the following menu path to select the required AFE and NN resources
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG DSP Enable --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
Graphics Libraries Configuration --->
...
AI Config --->
[*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
[*] Select AFE Resource
AFE (afe_res_2mic50mm) --->
[*] Select VAD Resource
VAD (vad_v7_200K) --->
[*] Select KWS Resource
KWS (kws_xiaoqiangxiaoqiang_nihaoxiaoqiang_v4_300K) --->
[*] Select ASR Resource
ASR (asr_cn_v8_2M) --->
[*] Select FST Resource
FST (fst_cn_cmd_ac40) --->
Use the resource packing tool under
{SDK}/component/aivoiceto pack the resources
../component/aivoice/tools/pack_resources/pack_resources_for_dsp.sh
This script will pack the resource files according to the configuration file {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project/menuconfig/.config.
Download the packed binary file
aivoice_models.binto the device
Import
{DSPSDK}/lib/aivoice/examples/full_flow_offlinesource in Xtensa Xplorer.Only need to import
ameba_dsp/in{DSPSDK}/lib/aivoice/examples/full_flow_offline/platformdirectory.Set software configurations and modify libraries such as AFE resource, KWS resource if needed.
Add include path (-I)
${workspace_loc}/../lib/aivoice/include
Add library search path (-L)
${workspace_loc}/../lib/aivoice/prebuilts/lib/ameba_dsp/$(TARGET_CONFIG)
${workspace_loc}/../lib/xa_nnlib/v2.3.0/bin/$(TARGET_CONFIG)/Release
${workspace_loc}/../lib/lib_hifi5/v3.1.0/bin/$(TARGET_CONFIG)
${workspace_loc}/../lib/tflite_micro/ameba_dsp-out/$(TARGET_CONFIG)
Add libraries (-l)
Using lib resources:
-laivoice -lafe_kernel -lkernel
-lafe_res_2mic50mm
-lvad_v7_200K
-lkws_xiaoqiangxiaoqiang_nihaoxiaoqiang_v4_300K
-lasr_cn_v8_2M
-lfst_cn_cmd_ac40
-lcJSON -ltomlc99 -ltflite_micro -lxa_nnlib -lhifi5_dsp -laivoice_hal
Using bin resources:
-laivoice -lafe_kernel -lkernel
-lcJSON -ltomlc99 -ltflite_micro
-lxa_nnlib -lhifi5_dsp -laivoice_hal
Attention
Follow the library order in this document since there are dependencies between libraries.
Refer to DSP project build steps in DSP Build to build the DSP image.
Refer to MCU project build steps in DSP Build to build the MCU images.
Pack AIVoice Binary Resources
If using AIVoice binary resources, follow these extra steps to prepare aivoice_models.bin:
Enter into SDK directory and run
env.shto set environment variables
cd {SDK}/
source env.sh
Run
ameba.pyto enter the configuration interface
ameba.py menuconfig RTL8713E
Navigate to the following menu path to select the required AFE and NN resources
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG DSP Enable --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
Graphics Libraries Configuration --->
...
AI Config --->
[*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
[*] Select AFE Resource
AFE (afe_res_2mic50mm) --->
[*] Select VAD Resource
VAD (vad_v7_200K) --->
[*] Select KWS Resource
KWS (kws_xiaoqiangxiaoqiang_nihaoxiaoqiang_v4_300K) --->
[*] Select ASR Resource
ASR (asr_cn_v8_2M) --->
[*] Select FST Resource
FST (fst_cn_cmd_ac40) --->
Use the resource packing tool under
{SDK}/component/aivoiceto pack the resources
../component/aivoice/tools/pack_resources/pack_resources_for_dsp.sh
This script will pack the resource files according to the configuration file {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project/menuconfig/.config.
Download the packed binary file
aivoice_models.binto the device

Add all aivoice example dependencies and linked resources into project
Using lib resources:
cd {DSPSDK}/lib/aivoice/examples/build_utils/ameba_dsp
./add_all_settings_to_project.sh {DSPSDK}/project/project_dsp/ full_flow_offline
Using bin resources:
cd {DSPSDK}/lib/aivoice/examples/build_utils/ameba_dsp
./add_all_settings_to_project.sh {DSPSDK}/project/project_dsp/ full_flow_offline --no_lib_resources
This will insert all the necessary dependencies and linke resources into the project makefile.
Build
dsp_all.bin, output directory{DSPSDK}/source/project/image/.
cd dsp/source/project/auto_build/
./auto_build.sh
Note
The default xtensa configuration is HIFI5_PROD_1123_asic_wUPG, can be modified via configName in {DSPSDK}/source/project/image/dsp_batch.xml.
Refer to MCU project build steps in DSP Build to build the MCU images.
Pack AIVoice Binary Resources
If using AIVoice binary resources, follow these extra steps to prepare aivoice_models.bin:
Enter into SDK directory and run
env.shto set environment variables
cd {SDK}/
source env.sh
Run
ameba.pyto enter the configuration interface
ameba.py menuconfig RTL8713E
Navigate to the following menu path to select the required AFE and NN resources
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG DSP Enable --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
Graphics Libraries Configuration --->
...
AI Config --->
[*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
[*] Select AFE Resource
AFE (afe_res_2mic50mm) --->
[*] Select VAD Resource
VAD (vad_v7_200K) --->
[*] Select KWS Resource
KWS (kws_xiaoqiangxiaoqiang_nihaoxiaoqiang_v4_300K) --->
[*] Select ASR Resource
ASR (asr_cn_v8_2M) --->
[*] Select FST Resource
FST (fst_cn_cmd_ac40) --->
Use the resource packing tool under
{SDK}/component/aivoiceto pack the resources
../component/aivoice/tools/pack_resources/pack_resources_for_dsp.sh
This script will pack the resource files according to the configuration file {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project/menuconfig/.config.
Download the packed binary file
aivoice_models.binto the device

Import
{DSPSDK}/lib/aivoice/examples/full_flow_offlinesource in Xtensa Xplorer.Only need to import
ameba_dsp/in{DSPSDK}/lib/aivoice/examples/full_flow_offline/platformdirectory.Set software configurations and modify libraries such as AFE resource, KWS resource if needed.
Add include path (-I)
${workspace_loc}/../lib/aivoice/include
Add library search path (-L)
${workspace_loc}/../lib/aivoice/prebuilts/lib/ameba_dsp/$(TARGET_CONFIG)
${workspace_loc}/../lib/xa_nnlib/v2.3.0/bin/$(TARGET_CONFIG)/Release
${workspace_loc}/../lib/lib_hifi5/v3.1.0/bin/$(TARGET_CONFIG)
${workspace_loc}/../lib/tflite_micro/ameba_dsp-out/$(TARGET_CONFIG)
Add libraries (-l)
Using lib resources:
-laivoice -lafe_kernel -lkernel
-lafe_res_2mic50mm
-lvad_v7_200K
-lkws_xiaoqiangxiaoqiang_nihaoxiaoqiang_v4_300K
-lasr_cn_v8_2M
-lfst_cn_cmd_ac40
-lcJSON -ltomlc99 -ltflite_micro -lxa_nnlib -lhifi5_dsp -laivoice_hal
Using bin resources:
-laivoice -lafe_kernel -lkernel
-lcJSON -ltomlc99 -ltflite_micro
-lxa_nnlib -lhifi5_dsp -laivoice_hal
Attention
Follow the library order in this document since there are dependencies between libraries.
Refer to DSP project build steps in DSP Build to build the DSP image.
Refer to MCU project build steps in DSP Build to build the MCU images.
Pack AIVoice Binary Resources
If using AIVoice binary resources, follow these extra steps to prepare aivoice_models.bin:
Enter into SDK directory and run
env.shto set environment variables
cd {SDK}/
source env.sh
Run
ameba.pyto enter the configuration interface
ameba.py menuconfig RTL8713E
Navigate to the following menu path to select the required AFE and NN resources
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG DSP Enable --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
Graphics Libraries Configuration --->
...
AI Config --->
[*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
[*] Select AFE Resource
AFE (afe_res_2mic50mm) --->
[*] Select VAD Resource
VAD (vad_v7_200K) --->
[*] Select KWS Resource
KWS (kws_xiaoqiangxiaoqiang_nihaoxiaoqiang_v4_300K) --->
[*] Select ASR Resource
ASR (asr_cn_v8_2M) --->
[*] Select FST Resource
FST (fst_cn_cmd_ac40) --->
Use the resource packing tool under
{SDK}/component/aivoiceto pack the resources
../component/aivoice/tools/pack_resources/pack_resources_for_dsp.sh
This script will pack the resource files according to the configuration file {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project/menuconfig/.config.
Download the packed binary file
aivoice_models.binto the device

Enter into SDK directory and run
env.shto set environment variables
cd {SDK}/
source env.sh
Run
ameba.pyto enter the configuration interface
ameba.py menuconfig RTL8730E
Navigate through menu path to enable TFLM Library and AIVoice
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG TrustZone --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
GUI Config --->
...
AI Config --->
[*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
Select AFE Resource according to hardware, default is
afe_res_2mic50mm
AI Config --->
[*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
Select AFE Resource
( ) afe_res_1mic
( ) afe_res_2mic30mm
(X) afe_res_2mic50mm
( ) afe_res_2mic70mm
Select KWS Resource, default is fixed keyword
xiao-qiang-xiao-qiangni-hao-xiao-qiang
AI Config --->
[*] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
Select AFE Resource
Select KWS Resource
(X) kws_res_xqxq
( ) kws_res_custom
Build image
ameba.py build -a full_flow_offline
(Optional) Modify yocto recipe
{LINUXSDK}/yocto/meta-realtek/meta-sdk/recipes-rtk/aivoice/rtk-aivoice-algo.bbto change library such as AFE resource, KWS resource if needed.Compile the aivoice algo image using bitbake:
bitbake rtk-aivoice-algo
Running and Expected Result
Download image to EVB, after running, the logs should display the algorithm results as follows:
[AFE] multi-kws-beam = 0, 1, 2
---------------------SPEECH COMMANDS---------------------
Command ID1, 打开空调
Command ID2, 关闭空调
Command ID3, 制冷模式
Command ID4, 制热模式
Command ID5, 加热模式
Command ID6, 送风模式
Command ID7, 除湿模式
Command ID8, 调到十六度
Command ID9, 调到十七度
Command ID10, 调到十八度
Command ID11, 调到十九度
Command ID12, 调到二十度
Command ID13, 调到二十一度
Command ID14, 调到二十二度
Command ID15, 调到二十三度
Command ID16, 调到二十四度
Command ID17, 调到二十五度
Command ID18, 调到二十六度
Command ID19, 调到二十七度
Command ID20, 调到二十八度
Command ID21, 调到二十九度
Command ID22, 调到三十度
Command ID23, 开高一度
Command ID24, 开低一度
Command ID25, 高速风
Command ID26, 中速风
Command ID27, 低速风
Command ID28, 增大风速
Command ID29, 减小风速
Command ID30, 自动风
Command ID31, 最大风量
Command ID32, 中等风量
Command ID33, 最小风量
Command ID34, 自动风量
Command ID35, 左右摆风
Command ID36, 上下摆风
Command ID37, 播放音乐
Command ID38, 暂停播放
Command ID39, 接听电话
Command ID40, 挂断电话
---------------------------------------------------------
[AIVOICE] rtk_aivoice version: v1.6.0#S87db3f2#N89da3ed#Ad90cdbe
[AIVOICE] rtk_aivoice_model afe version: afe_2mic_asr_v1.5_AfePara_2mic50_v2.0_bf_v0.0_20250401
[AIVOICE] rtk_aivoice_model vad version: vad_v7_opt
[AIVOICE] rtk_aivoice_model kws version: kws_xqxq_v4.1_opt
[AIVOICE] rtk_aivoice_model asr version: asr_cn_v8_opt
[AIVOICE] rtk_aivoice_log_format version: v2
[user] afe output 1 channels raw audio, others: {"abnormal_flag":0,"ssl_angle":-10}
[AIVOICE] [KWS] result: {"id":2,"keyword":"ni-hao-xiao-qiang","score":0.766761064529419}
[user] wakeup. {"id":2,"keyword":"ni-hao-xiao-qiang","score":0.766761064529419}
[user] voice angle 90.0
[user] vad. status = 1, offset = 425
[user] vad. status = 0, offset = 1865
[AIVOICE] [ASR] result: {"type":0,"commands":[{"rec":"打开空调","id":1}]}
[user] asr. {"type":0,"commands":[{"rec":"打开空调","id":1}]}
[user] voice angle 90.0
[user] vad. status = 1, offset = 525
[AIVOICE] [KWS] result: {"id":2,"keyword":"ni-hao-xiao-qiang","score":0.81332826614379883}
[user] wakeup. {"id":2,"keyword":"ni-hao-xiao-qiang","score":0.81332826614379883}
[user] voice angle 90.0
[user] vad. status = 1, offset = 445
[user] vad. status = 0, offset = 1765
[AIVOICE] [ASR] result: {"type":0,"commands":[{"rec":"播放音乐","id":37}]}
[user] asr. {"type":0,"commands":[{"rec":"播放音乐","id":37}]}
[user] voice angle 90.0
Example 2: SpeechMind Real-Time Example (Using Microphone Input)
SpeechMind is an intelligent voice assistant framework that integrates AIVoice algorithms, audio capture, and player functionalities. This example demonstrates how to use the SpeechMind framework for real-time voice wake-up and recognition. The example uses the preset command words in the SDK. If custom command words are required, please refer to the Custom Command Guide .
More Information
Introduction and APIs: SpeechMind
Github repository: speechmind
Hardware Requirements
The development board must have:
Two microphones with a 50mm spacing
One feedback signal path
An externally connected speaker
Attention
Ensure that the configured microphones match the development board; otherwise, the algorithm may fail or degrade in performance. Configuration can be found in speechmind/src/audio_capture.c
Build Example
This example uses precompiled DSP firmware provided in the AIVoice repository + AIVoice binary resource firmware. For custom DSP firmware builds, refer to build steps of example 1 in Example and code aivoice/examples/speechmind_demo .
Package the response audio directory into a virtual file system firmware
tts.bin. Refer to Virtual File System for more details.
cd {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project
../tools/image_scripts/vfs.py -t LITTLEFS -dir ../component/application/speechmind/res/tts -out tts.bin
Modify Flash layout in
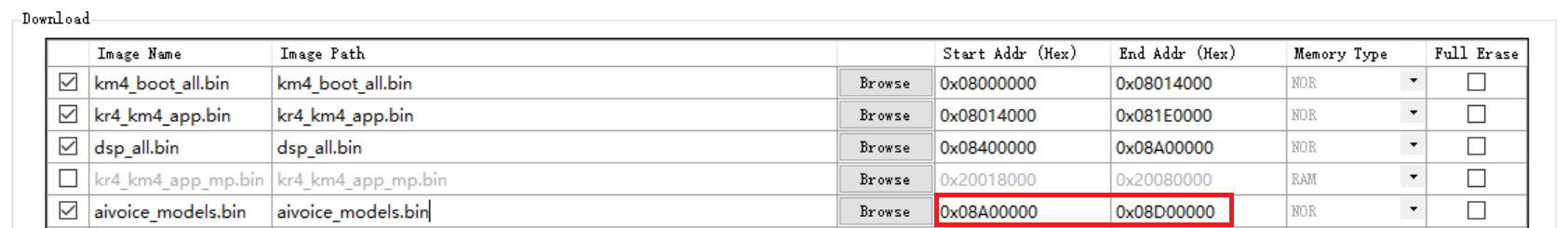
{SDK}/component/soc/usrcfg/amebalite/ameba_flashcfg.caccording to the size oftts.binand start address ofaivoice_models.bin(0x08A00000 in precompiled DSP firmware). Refer to Flash Layout for more details.
#ifdef CONFIG_SOC_SOLO
#else
FlashLayoutInfo_TypeDef Flash_Layout[] = {
/* Region_Type, [StartAddr, EndAddr] */
{IMG_BOOT, 0x08000000, 0x08013FFF}, //Boot Manifest(4K) + KM4 Bootloader(76K)
//Users should modify below according to their own memory
{IMG_APP_OTA1, 0x08014000, 0x081FFFFF}, //Certificate(4K) + Manifest(4K) + KR4 & KM4 Application OTA1 + RDP IMG OTA1
{IMG_BOOT_OTA2, 0x08200000, 0x08213FFF}, //Boot Manifest(4K) + KM4 Bootloader(76K) OTA
{IMG_APP_OTA2, 0x08214000, 0x083DCFFF}, //Certificate(4K) + Manifest(4K) + KR4 & KM4 Application OTA2 + RDP IMG OTA2
{FTL, 0x083DD000, 0x083DFFFF}, //FTL for BT(>=12K), The start offset of flash pages which is allocated to FTL physical map.
{VFS1, 0x083E0000, 0x084C9FFF}, //VFS region 1 (936K)
{IMG_DSP, 0x084CA000, 0x086FFFFF}, //Manifest(4K) + DSP IMG, only one DSP region in layout
{VFS2, 0xFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFF}, //VFS region 2
{USER, 0x08A00000, 0xFFFFFFFF}, //reserve for user
/* End */
{0xFF, 0xFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFF},
};
Note
In this example
tts.binsize is 936 K, so VFS1 end address modified to 0x083E0000 + 936K = 0x084C9FFFNo overlap allowed between image addresses, so IMG_DSP start address modified to 0x084C9FFF + 1 = 0x084CA000
Switch to the SDK’s GCC project directory and run
menuconfig.pyto enter the configuration interface
cd {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project
./menuconfig.py
Enable DSP through menu navigation
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG DSP Enable --->
[*] Enable DSP
Config Link through menu navigation
Branch master:
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG Link Option --->
IMG2(Application) running on FLASH or PSRAM?
(X) FLASH
( ) PSRAM
IMG2 Data and Heap in SRAM or PSRAM? --->
( ) SRAM
(X) PSRAM
Branch v1.1:
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG Link Option --->
IMG2(Application) running on FLASH or PSRAM?
(X) CodeInXip_DataHeapInPsram
( ) CodeInPsram_DataHeapInSram
( ) CodeInPsram_DataHeapInPsram
( ) CodeInXip_DataHeapInSram
Enable VFS LITTLEFS
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG VFS --->
[*] Enable VFS LITTLEFS
Enable AIVoice (select algorithm version as needed)
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG TrustZone --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
GUI Config --->
...
AI Config --->
[ ] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
Enable Speechmind
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG TrustZone --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
GUI Config --->
...
AI Config --->
[ ] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
[*] Enable SpeechMind
Build KM4 and KR4 firmware
./build.py
Prepare AIVoice resource firmware
../component/aivoice/tools/pack_resources/pack_resources_for_dsp.sh
Download image using Flash Programming Tool
km4_boot_all.bin: Default address
kr4_km4_app.bin: Default address
tts.bin: Address matches VFS1 in Step 2
dsp_all.bin: Use
aivoice/prebuilts/image/ameba_dsp/${TARGET}/dsp_all.bin(select TARGET as needed). Address matches IMG_DSP in Step 2aivoice_models.bin: Address matches USER region in Step 2

This example uses precompiled DSP firmware provided in the AIVoice repository + AIVoice binary resource firmware. For custom DSP firmware builds, refer to build steps of example 1 in Example and code aivoice/examples/speechmind_demo .
Package the response audio directory into a virtual file system firmware
tts.bin. Refer to Virtual File System for more details.
cd {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project
../tools/image_scripts/vfs.py -t LITTLEFS -dir ../component/application/speechmind/res/tts -out tts.bin
Modify Flash layout in
{SDK}/component/soc/usrcfg/amebalite/ameba_flashcfg.caccording to the size oftts.binand start address ofaivoice_models.bin(0x08A00000 in precompiled DSP firmware). Refer to Flash Layout for more details.
#ifdef CONFIG_SOC_SOLO
#else
FlashLayoutInfo_TypeDef Flash_Layout[] = {
/* Region_Type, [StartAddr, EndAddr] */
{IMG_BOOT, 0x08000000, 0x08013FFF}, //Boot Manifest(4K) + KM4 Bootloader(76K)
//Users should modify below according to their own memory
{IMG_APP_OTA1, 0x08014000, 0x081FFFFF}, //Certificate(4K) + Manifest(4K) + KR4 & KM4 Application OTA1 + RDP IMG OTA1
{IMG_BOOT_OTA2, 0x08200000, 0x08213FFF}, //Boot Manifest(4K) + KM4 Bootloader(76K) OTA
{IMG_APP_OTA2, 0x08214000, 0x083DCFFF}, //Certificate(4K) + Manifest(4K) + KR4 & KM4 Application OTA2 + RDP IMG OTA2
{FTL, 0x083DD000, 0x083DFFFF}, //FTL for BT(>=12K), The start offset of flash pages which is allocated to FTL physical map.
{VFS1, 0x083E0000, 0x084C9FFF}, //VFS region 1 (936K)
{IMG_DSP, 0x084CA000, 0x086FFFFF}, //Manifest(4K) + DSP IMG, only one DSP region in layout
{VFS2, 0xFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFF}, //VFS region 2
{USER, 0x08A00000, 0xFFFFFFFF}, //reserve for user
/* End */
{0xFF, 0xFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFF},
};
Note
In this example
tts.binsize is 936 K, so VFS1 end address modified to 0x083E0000 + 936K = 0x084C9FFFNo overlap allowed between image addresses, so IMG_DSP start address modified to 0x084C9FFF + 1 = 0x084CA000
Switch to the SDK’s GCC project directory and run
menuconfig.pyto enter the configuration interface
cd {SDK}/amebalite_gcc_project
./menuconfig.py
Enable DSP through menu navigation
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG DSP Enable --->
[*] Enable DSP
Config Link through menu navigation
Branch master:
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG Link Option --->
IMG2(Application) running on FLASH or PSRAM?
(X) FLASH
( ) PSRAM
IMG2 Data and Heap in SRAM or PSRAM? --->
( ) SRAM
(X) PSRAM
Branch v1.1:
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG Link Option --->
IMG2(Application) running on FLASH or PSRAM?
(X) CodeInXip_DataHeapInPsram
( ) CodeInPsram_DataHeapInSram
( ) CodeInPsram_DataHeapInPsram
( ) CodeInXip_DataHeapInSram
Enable VFS LITTLEFS
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG VFS --->
[*] Enable VFS LITTLEFS
Enable AIVoice (select algorithm version as needed)
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG TrustZone --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
GUI Config --->
...
AI Config --->
[ ] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
Enable Speechmind
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG TrustZone --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
GUI Config --->
...
AI Config --->
[ ] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
[*] Enable SpeechMind
Build KM4 and KR4 firmware
./build.py
Prepare AIVoice resource firmware
../component/aivoice/tools/pack_resources/pack_resources_for_dsp.sh
Download image using Flash Programming Tool
km4_boot_all.bin: Default address
kr4_km4_app.bin: Default address
tts.bin: Address matches VFS1 in Step 2
dsp_all.bin: Use
aivoice/prebuilts/image/ameba_dsp/${TARGET}/dsp_all.bin(select TARGET as needed). Address matches IMG_DSP in Step 2aivoice_models.bin: Address matches USER region in Step 2

FreeRTOS
Package the response audio directory into a virtual file system firmware
tts.bin. Refer to Virtual File System for more details.
cd {SDK}/amebasmart_gcc_project
../tools/image_scripts/vfs.py -t LITTLEFS -dir ../component/application/speechmind/res/tts -out tts.bin
Modify Flash layout in file
{SDK}/component/soc/usrcfg/amebasmart/ameba_flashcfg.caccording to the size oftts.bin. Refer to Flash Layout for more details.
FlashLayoutInfo_TypeDef Flash_Layout[] = {
/* Region_Type, [StartAddr, EndAddr] */
{IMG_BOOT, 0x08000000, 0x0801FFFF}, //Boot Manifest(4K) + KM4 Bootloader(124K)
//Users should modify below according to their own memory
{IMG_APP_OTA1, 0x08020000, 0x082FFFFF}, //Certificate(4K) + Manifest(4K) + KM0 & KM4 & CA32 Application OTA1 + RDP IMG OTA1
// + AP IMG OTA1
{IMG_BOOT_OTA2, 0x08300000, 0x0833FFFF}, //Boot Manifest(4K) + KM4 Bootloader(252K) OTA
{IMG_APP_OTA2, 0x08340000, 0x0861FFFF}, //Certificate(4K) + Manifest(4K) + KM0 & KM4 & CA32 Application OTA2 + RDP IMG OTA2
// + AP IMG OTA2
{FTL, 0x08620000, 0x08622FFF}, //FTL for BT(>=12K), The start offset of flash pages which is allocated to FTL physical map.
{VFS1, 0x08623000, 0x0870CFFF}, //VFS region 1 (936K)
{VFS2, 0xFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFF}, //VFS region 2
{USER, 0xFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFF}, //reserve for user
/* End */
{0xFF, 0xFFFFFFFF, 0xFFFFFFFF},
};
Note
In this example
tts.binsize is 936 K, so VFS1 end address modified to 0x08623000 + 936K = 0x0870CFFF
Switch to the SDK’s GCC project directory and run
menuconfig.pyto enter the configuration interface
cd {SDK}/amebasmart_gcc_project
./menuconfig.py
Select run application from Flash through menu navigation
Branch master:
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG Link Option --->
IMG2(Application) running on PSRAM or FLASH? --->
( ) PSRAM
(X) FLASH
Branch v1.1:
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG BOOT OPTION --->
[*] XIP_FLASH
Enable VFS LITTLEFS
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG VFS --->
[*] Enable VFS LITTLEFS
Enable AIVoice (select algorithm version as needed)
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG TrustZone --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
GUI Config --->
...
AI Config --->
[ ] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
Enable Speechmind
--------MENUCONFIG FOR General---------
CONFIG TrustZone --->
...
CONFIG APPLICATION --->
GUI Config --->
...
AI Config --->
[ ] Enable TFLITE MICRO
[*] Enable AIVoice
[*] Enable SpeechMind
Choose single core
MENUCONFIG FOR CA32 CONFIG --->
...
CONFIG SMP --->
Select Core Num --->
( ) DUAL
(X) SINGLE
Build image
./build.py
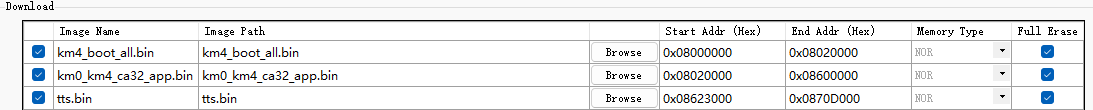
Download image using Flash Program Tool
km4_boot_all.bin: Default address
km0_km4_ca32_app.bin: Address 0x08020000, 0x08600000
tts.bin: Address matching VFS1 defined in Step 2
Running and Expected Results
After downloading the images onto the development board, the following voice interaction features can be tested:
Voice Wake-Up
Wake up the device by saying
xiao-qiang-xiao-qiangorni-hao-xiao-qiang. If successful, logs will be printed, and the response audioMaster, I'm herewill be played.Timeout
If no interaction occurs after wake-up, the device will announce
Master, I'll step back for now. Wake me up if needed. Further interaction requires re-wake-up. The timeout duration can be adjusted inspeech_mind.cvia:aivoice_param.timeout = 10;
Command Recognition
After wake-up, continuous interaction is possible using voice commands like
Turn on the air conditionerorTurn off the air conditioner. If recognized, logs will be printed, and corresponding response audio will be played. The supported command list can be found in the boot-up logs.Wake-Up Interruption (Echo Cancellation)
After wake-up, say
Play musicto start playback. During playback, wake-up words or commands can interrupt the music. If recognized, logs will be printed, and playback will pause to play the response audio.Sound Source Localization (SSL)
When SSL is enabled, the device detects the speaker’s direction after each wake-up. The angle will be logged, and the response audio
xx degreeswill be played. SSL can be enabled/disabled inspeech_mind.cvia:#define ENABLE_SSL_DOA 1
Glossary
- AEC
Acoustic Echo Cancellation, or echo cancellation, refers to removing the echo signal from the input signal. The echo signal is generated by a sound played through the speaker of the device then captured by the microphone.
- AFE
Audio Front End, refers to a combination of modules for preprocessing raw audio signals. It’s usually performed to improve the quality of speech signal before the voice interaction, including several speech enhancement algorithms.
- AGC
Automatic Gain Control, an algorithm that dynamically controls the gain of a signal and automatically adjust the amplitude to maintain an optimal signal strength.
- ASR
Automatic Speech Recognition, or Speech-to-Text, refers to recognition of spoken language from audio into text. It can be used to build voice-user interface to enable spoken human interaction with AI devices.
- BF
BeamForming, refers to a spatial filter designed for a microphone array to enhance the signal from a specific direction and attenuate signals from other directions.
- KWS
Keyword Spotting, or wakeup word detection, refers to identifying specific keywords from audio. It is usually the first step in a voice interaction system. The device will enter the state of waiting voice commands after detecting the keyword.
- NN
Neural Network, is a machine learning model used for various task in artificial intelligence. Neural networks rely on training data to learn and improve their accuracy.
- NS
Noise Suppression, or noise reduction, refers to suppressing ambient noises in the signal to enhance the speech signal, especially stationary noises.
- RES
Residual Echo Suppression, refers to suppressing the remained echo signal after AEC processing. It is a postfilter for AEC.
- SSL
Sound Source Localization, or direction of arrival (DOA), refers to estimating the spatial location of a sound source using a microphone array.
- TTS
Text-To-Speech, or speech synthesis, is a technology that converts text into spoken audio. It can be used in any speech-enabled application that requires converting text to speech imitating human voice.
- VAD
Voice Activity Detection, or speech activity detection, is a binary classifier to detect the presence or absence of human speech. It is widely used in speech enhancement, ASR system etc, and can also be used to deactivate some processes during non-speech section of an audio session, saving on computation or bandwidth.

