DualChip-Coex Function
DualChip-Coex Architecture
DualChip-Coex primarily refers to coexistence between a WiFi SoC and external devices. The external devices include those using the Bluetooth protocol or the 802.15.4 protocol. DualChip-Coex supports scenarios where the WiFi SoC and the external device share an antenna, as well as scenarios where the WiFi SoC and the external device use separate antennas.
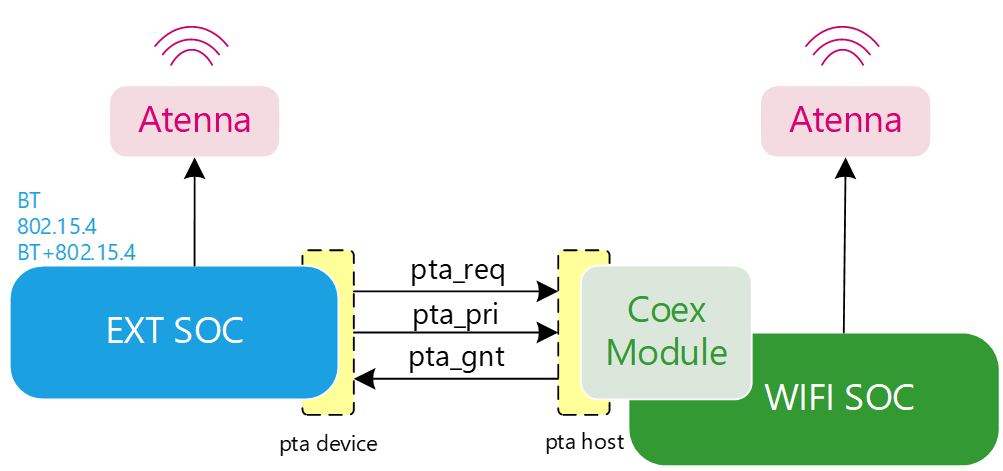
DualChip-Coex Dual-Atenna Architecture
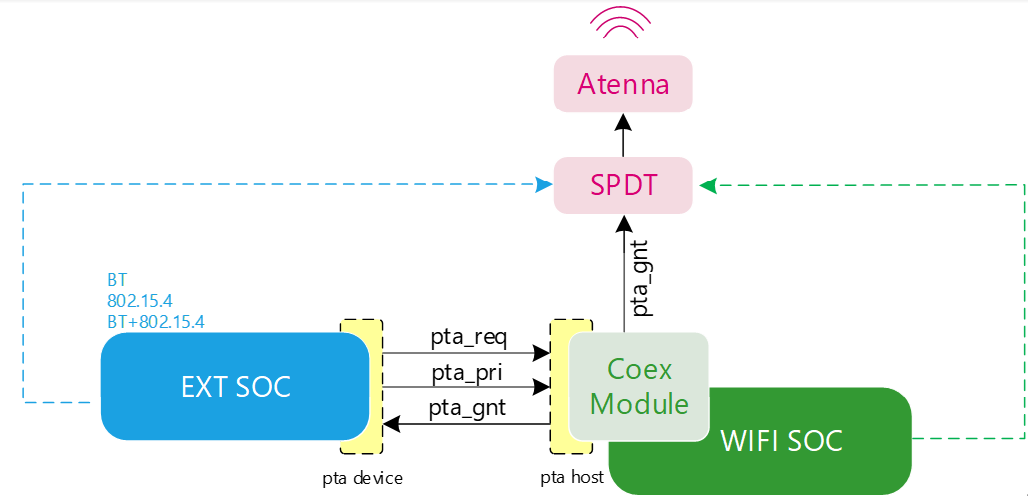
DualChip-Coex Single-Atenna Architecture
To use the WiFi SoC’s Dualchip-Coex feature, the external protocol device must support the PTA 3-wire protocol (see the following sections). As shown in the Dualchip-Coex Architecture above, the coexistence module receives the pta_req and pta_pri signals, performs arbitration with the current WL module’s requests, and finally outputs the arbitration result to the external protocol device via the pta_gnt signal.
Coexistence Strategy
Whether it is the SingleChip-Coex or DualChip-Coex feature, the coexistence mechanism allocates RF module resources based on the priority of each packet from the requesting modules. The coexistence strategies are mainly divided into two types:
PTA strategy: Pairwise arbitration between different requesting modules based on packet priority, with the arbitration result output to the requesting modules through the wlan_act (or pta_gnt) signal.
TDMA strategy: Different requesting modules use the resource according to assigned time slots; for example, during the WL time slot, WL is selected with relatively higher priority; during the BT time slot, BT is selected with relatively higher priority; and during the external device time slot, the external device is selected with relatively higher priority.
Currently, the DualChip-Coex feature primarily uses the PTA strategy, while TDMA is under planning.
PTA 3-Wire Protocol
As shown in the figure below, the PTA 3-wire protocol can be understood through the following concepts.
PTA device: Ext Chip
PTA host: WiFi SoC
REQUEST: Indicates whether the PTA device side has a request. If the REQUEST signal is set high, it means the PTA device has initiated a request.
PRIORITY: Indicates whether the request from the PTA device side is of high or low priority. It can also indicate whether the request is for a TX (transmit) operation or an RX (receive) operation.
T1 (priority detect time): The time window after the REQUEST signal is asserted during which the priority of the request can be determined. If PRIORITY is set high within the T1 period after REQUEST is asserted, it indicates that the request is of high priority; otherwise, it is of low priority.
T2 (trx detect time): The time window after the T1 period during which the type of transfer action can be determined. After T1 ends, if PRIORITY remains high or changes to high during T2, it indicates that the request is a TX operation; if PRIORITY remains low or changes to low during T2, it indicates that the request is an RX operation.
T1 and T2: Provided by the PTA device side; the PTA host side follows the configuration.
GNT: Indicates the arbitration signal given by the PTA host side to the PTA device side. If it is set low, it means the request from the PTA device can proceed; otherwise, it cannot.
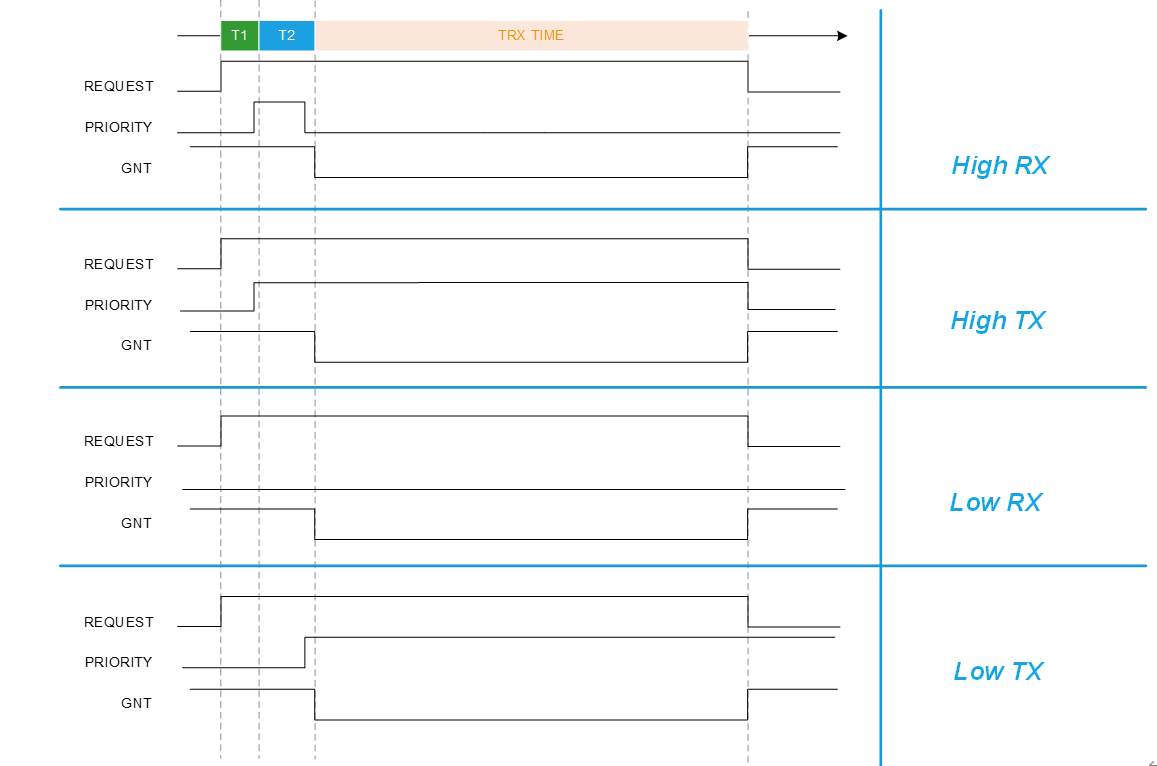
PTA 3-Wire Protocol
WiFi SOC Configuration
When the WiFi SoC needs to connect to an external BT or 802.15.4 device, you need to configure it in menuconfig. The configuration description is as follows.
Enable Ext Coex Support
To enable the WiFi SoC to support the above Dualchip-Coex functionality, enable “Coex Support” as shown in the figure.
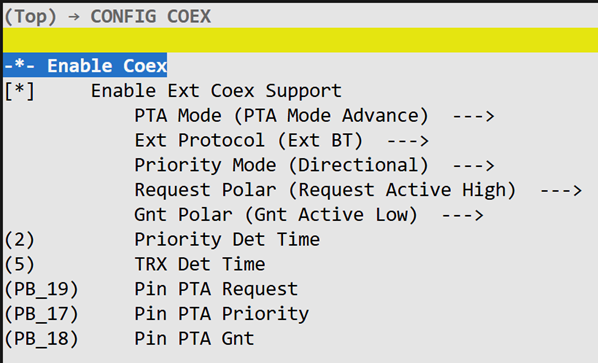
Enable Ext Coex Support
PTA Mode
If the external device uses the 802.15.4 protocol, it is recommended to prioritize “PTA Mode Simple”. If the external device uses the BT protocol and the WiFi SoC’s internal BT is not used, prioritize “PTA Mode Advance”; otherwise, choose “PTA Mode Simple”.
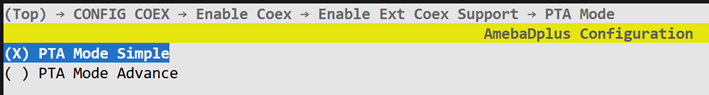
PTA Mode
Ext Protocal
If the external device uses the 802.15.4 protocol, select “Ext WPAN”. If the external device uses the BT protocol, select “Ext BT”. If the external device uses both 802.15.4 and BT and they need to coexist, select “Ext BT&WPAN”.
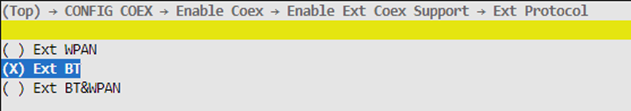
Ext Protocol
Priority Mode
This option is configurable only when PTA Mode is set to “PTA Mode Simple”. If the PRIORITY signal in the PTA 3-wire protocol supports identifying TRX (transmit/receive direction), select “Directional”; otherwise, select “Static”.
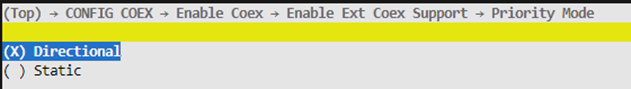
Priority Mode
Request Polar
This option is configurable only when PTA Mode is set to “PTA Mode Simple”. If the REQUEST signal is low by default and goes high when there is a request, select “Request Active High”; otherwise, select “Request Active Low”.
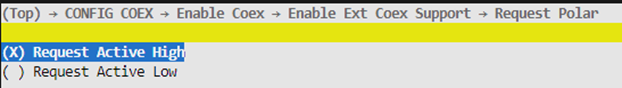
Request Polar
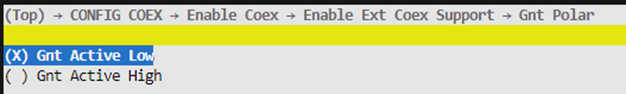
Gnt Polar
This option is configurable only when PTA Mode is set to “PTA Mode Simple”. If the GNT signal is high by default and goes low when arbitration grants the external device, select “Gnt Active Low”; otherwise, select “Gnt Active High”.
Gnt Polar
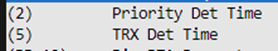
Priority Det Time/TRX Det Time
“Priority Det Time” corresponds to T1 in the PTA 3‑wire protocol section, and “TRX Det Time” corresponds to T2.
Det Time
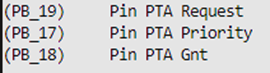
Pinmux Setting
When the Wi‑Fi SoC acts as the PTA Host, it needs to configure pinmux for the incoming signals pta_request/pta_pri/pta_gnt, and suitable pins can be selected via the following menuconfig options.
RTL8721Dx Pinmux Setting

