WHC Wi-Fi Slim Host Driver Porting
Driver Porting
FullMAC is currently tested and validated on Linux kernels 5.4 and 5.10. If you encounter compilation issues on other kernel versions, please contact us.
Note
SPI initiates data transfer immediately after CS pin is pulled low and CLK is detected. Corner cases may occur during bus busy states.
Testing shows adding a 7μs delay between CS low and host CLK push ensures safe data transmission.
However, older SPI drivers without spi_delay support may require direct code modification.
Prerequisites
Install dependencies on Linux:
sudo apt-get install build-essential
sudo apt install dhcpcd hostapd dhcpd
Interface Activation
Linux PC: Skip this step
Raspberry Pi:
Configure SDIO via
dtoverlay.For Raspberry Pi 4:
sudo dtoverlay sdio poll_once=off
For Raspberry Pi 5:
sudo dtoverlay sdio
In directory
/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux, run the following cmd.nanandp2pis an optional parameter and should be added only when Wi-Fi NAN and Wi-Fi P2P needs to be enabled../fullmac_setup.sh sdio [nan] [p2p]
./fullmac_setup.sh spi [nan] [p2p]
./fullmac_setup.sh usb [nan] [p2p]
Select 1 or 2 based on the host operation mode
choose target host mode: 1) Fat host with cfg80211 2) Slim host without cfg80211 choose target host mode:
Copy
whc_host_linuxto Linux kernel source treeOpen new terminal and compile
cd {driver_path}/whc_host_linux make
Driver Loading
Module Path:
/whc_host_linux/sdio/fullmac_sdio.kosudo su cp sdio/fullmac_sdio.ko /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/ depmod -a modprobe fullmac_sdio
Module Path:
/whc_host_linux/spi/fullmac_spi.kosudo su cp spi/fullmac_spi.ko /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/ depmod -a modprobe fullmac_spi
Module Path:
/whc_host_linux/usb/fullmac_usb.kosudo su cp usb/fullmac_usb.ko /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/ depmod -a modprobe fullmac_usb
After successful loading, run
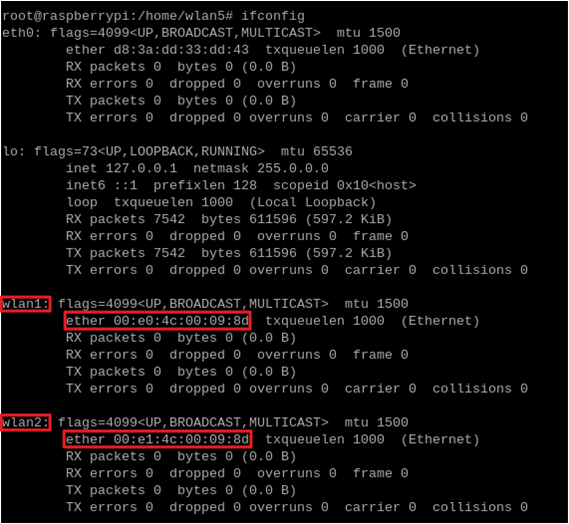
ifconfigto verify Wi-Fi devices.Sample Output:
Station mode MAC prefix:
00:e0:4cSoftAP mode MAC prefix:
00:e1:4c
Programming Guide for Ameba as FullMAC Host
Environment Setup
Execute the configuration tool in the directory
{SDK}/amebadplus_gcc_project(Top) -> CONFIG WHC INTF -> WHC_MODE ----Configuration---- ( ) WHC_IPC ( ) FULLMAC_DEV (X) FULLMAC_HOST (Top) -> CONFIG WHC INTF -> FULLMAC HOST config ----Configuration---- (X) Support WHC CMD PATH (X) Support WHC WIFI API PATH
Firmware Compilation
Generate target files:
./build.py
Output files:
km4_boot_all.binkm0_km4_app.bin
Firmware Burning
Use the dedicated burning tool to write the firmware to the development board
Third-party Platform Porting
When using other Host chips, the component/os/freertos directory must be ported to the target system.
Demo Introduction
In Slim Host mode, standard Wi-Fi APIs are unavailable, and the CUST_PATH must be used for Wi-Fi control. Therefore, we need to develop a non-standard demo program for demonstration purposes.
The application supports bidirectional communication between User Space and Kernel Space through two command types:
Kernel-Level Configuration
setmac:Configure device MAC addressnetifon:Activate network interface carrier
Device-Level Control
getmac: Retrieve device MAC addressgetip: Retrieve device IP configurationsetrdy: Notify device statetickps: Tickless Power Save command, Notify the device that it can enter low-power modewifion: Notify device to initialize WiFi
The communication architecture is shown below:
Supported Commands
Command Format |
Description |
init |
Initialize kernel Netlink communication channel |
getmac <device_idx> |
Retrieve specified device MAC address device_idx: Device port index (0 or 1 only)
|
getip <device_idx> |
Retrieve device network layer configuration device_idx: Device port index (same as getmac) |
setrdy <state> |
Notifies the device of the host state state:ready (active) or unready (inactive) |
setmac <device_idx> <mac> |
Configure interface hardware address
|
netifon <device_idx> |
Activate physical layer carrier device_idx: Device port index (same as getmac) |
tickps <subtype> |
Tickless Power Save command subtype: Tickless Power Save command type
|
wifion |
Notify device to initialize WiFi |
connect <ssid> <pw> |
Notify device to connect
|
dhcp |
Notify device for IP negotiation |
Compilation and Execution
# Enter module directory
cd ${SDK}/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux/app
# Compile executable
make
# Run with privileged mode
sudo ./whc_slim_host_demo
The communication architecture of application is shown below:
Supported Commands
Command Format |
Description |
whc hostrtos |
Configure Host OS mode |
whc getmac <device_idx> |
Retrieve specified device MAC address device_idx: Device port index (0 or 1 only)
|
whc getip <device_idx> |
Retrieve device network layer configuration device_idx: Device port index (same as getmac) |
whc setrdy <state> |
Notifies the device of the host state state:ready (active) or unready (inactive) |
whc wifion |
Notify device to initialize WiFi |
whc connect <ssid> <pw> |
Notify device to connect
|
whc dhcp |
Notify device for IP negotiation |
whc scan |
Initiate network scanning on the device. |
Functional Verification And Demo
Run the demo
cd ${SDK}/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux/app sudo ./whc_slim_host_demo
Execute initialization sequence in demo
> init > wifion > getmac 0 00:E0:4C:XX:XX:XX > setmac 0 00:E0:4C:XX:XX:XX
Perform Wi-Fi scan in demo
> scanEstablish wireless connection in demo
> netifon 0 > connect ap_test 12345678
Note
ap_testrepresents the target AP’s SSID,12345678is the target AP’s password. Omit password parameter for open networks.
Execute the following command in the terminal to dynamically obtain an IP address
> dhcpcd wlanX
Note
wlanXis the name of the wireless interface device, execute ifconfig -a` in the terminal to retrieve its informationNetwork Testing
ping 192.168.x.x
Run the demo
cd ${SDK}/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux/app sudo ./whc_slim_host_demo
Execute initialization sequence in demo
> init > wifion > getmac 0 00:E0:4C:XX:XX:XX > setmac 0 00:E0:4C:XX:XX:XX
Perform Wi-Fi scan in demo
> scanEstablish wireless connection in demo
> netifon 0 > connect ap_test 12345678
Note
ap_testrepresents the target AP’s SSID,12345678is the target AP’s password. Omit password parameter for open networks.
Retrieve IP configuration from device
> getip 0
Configure host network interface
sudo ip addr add 192.168.x.x/24 dev wlanX sudo ip link set wlanX up sudo ip route add default via 192.168.x.x dev wlanX
Note
wlanXis the name of the wireless interface device, execute ifconfig -a` in the terminal to retrieve its informationValidate interface status
> netifon 0
Network Validation
ping 192.168.x.x
Initial Configuration
Enter the following commands in the serial terminal to execute the initialization sequence:
> whc hostrtos > whc wifion > whc getmac
Connect to Wireless Network
Enter the following command in the serial terminal to perform a WiFi scan
> whc scan
Enter the following command in the serial terminal to establish a wireless connection:
> whc connect ap_test 12345678
Note
ap_testrepresents the target AP’s SSID,12345678is the target AP’s password. Omit password parameter for open networks.Network Testing
AT+WLPING=192.168.x.x