Wi-Fi
Overview
This chip contains three cores:
LP: low power processor, KM0, and the firmware of Wi-Fi works on it.
NP: Network processor, KM4, and the driver of Wi-Fi works on it.
AP: Application processor, CA32, and the FullMAC works on it. The FullMAC driver is an adaptive driver between cfg80211 in Linux kernel and INIC device in FreeRTOS.
Architecture
The FullMAC is new Wi-Fi driver based on the CFG80211 interface. So it supports wpa_supplicant, hostapd, iwconfig, and so on. The driver sends the command to IPC INIC device on KM4 with IPC message and receives the event from IPC INIC device. Therefore, the FullMAC driver will convert the command and structure from CFG80211 to the IPC INIC commands and data type, and the events from IPC INIC device also are converted the format of CFG80211 and reported to the Linux kernel.
There are two IPC messages in FullMAC driver. One is the API message, and another is the data message. The API message is used to send command or receive event to manage the Wi-Fi. The data message is used to send or receive the data frame of Wi-Fi. So the former is low speed and the latter is high speed.
Configuration
Configuration in Kernel
Run the following command in build directory of project to open the configuration of kernel.
bitbake virtual/kernel -c menuconfig
Enabling Ameba IPC
The Wi-Fi driver in Linux is based on Ameba IPC’s driver, so the IPC’s driver must be enabled for Wi-Fi driver. Of course, this option is enabled if you choose Fullmac for rtl8730e to yes.
Device Drivers --->
<*> Drivers for Realtek --->
[*] Ameba IPC
Enabling CFG80211
This configuration is base of Wi-Fi driver based on cfg80211, and they are enabled by default.
[*] Networking support --->
-*- Wireless --->
<*> cfg80211 - wireless configuration API
[*] enable powersave by default
[*] support CRDA
[*] cfg80211 wireless extensions compatibility
Enabling FullMAC Driver
This configuration is used to enable Wi-Fi driver in Linux kernel, and it is enabled by default.
Device Drivers --->
<*> Drivers for Realtek --->
<*> CFG80211 WiFi FULLMAC drivers --->
<*> Fullmac for rtl8730e
Function
There are only two ports in Wi-Fi driver, wlan0 and wlan1. The wlan0 must work in station mode only and the wlan1 must work in access point (AP) mode only.
Supplicant and Hostap
This is NL80211 version driver and it supports wpa_supplicant and hostapd.
Station Mode
wpa_supplicant
wpa_supplicant is a cross-platform supplicant with support for WPA, WPA2 and WPA3 (IEEE 802.11i). It is the IEEE 802.1X/WPA component that is used in the client stations. It implements key negotiation with a WPA authenticator and it controls the roaming and IEEE 802.11 authentication/association of the wireless driver.
wpa_supplicant.conf
wpa_supplicant is configured using a text file that lists all accepted networks and security policies, including pre-shared keys. See the example configuration file, probably in /etc/wifi, for detailed information about the configuration format and supported fields.
All file paths in this configuration file should use full (absolute, not relative to working directory) path in order to allow working directory to be changed. This can happen if wpa_supplicant is run in the background.
Changes to configuration file can be reloaded be sending SIGHUP signal to wpa_supplicant (killall -HUP wpa_supplicant). Similarly, reloading can be triggered with the wpa_cli reconfigure command.
Configuration file can include one or more network blocks, e.g., one for each used SSID. wpa_supplicant will automatically select the best network based on the order of network blocks in the configuration file, network security level (WPA/WPA2 is preferred), and signal strength.
Below example is two examples for WPA-Personal (PSK) as home network and WPA-Enterprise with EAP-TLS as work network.
# allow frontend (e.g., wpa_cli) to be used by all users in 'wheel' group
ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=wheel
#
# home network; allow all valid ciphers
update_config=1
wowlan_triggers=any
network={
ssid="home"
scan_ssid=1
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
psk="very secret passphrase"
}
#
# work network; use EAP-TLS with WPA; allow only CCMP and TKIP ciphers
network={
ssid="work"
scan_ssid=1
key_mgmt=WPA-EAP
pairwise=CCMP TKIP
group=CCMP TKIP
eap=TLS
identity="user@example.com"
ca_cert="/etc/cert/ca.pem"
client_cert="/etc/cert/user.pem"
private_key="/etc/cert/user.prv"
private_key_passwd="password"
}
If the configuration want to be saved, update_config=1 should be added in the /etc/wifi/wpa_supplicant.conf, or to use command wpa_cli -i wlan0 set update_config 1.
If the enable wowlan function, wowlan_triggers=any should be added in the /etc/wifi/wpa_supplicant.conf, or to use command wpa_cli -i wlan0 set wowlan_triggers any. Otherwise, the supplicant will disconnect from AP when to suspend.
run wpa_supplicant
Below command can run wpa_supplicant on nl80211 interface and wlan0 port. It will use the configuration file /etc/wifi/wpa_supplicant.conf and run in background.
wpa_supplicant -D nl80211 -i wlan0 -c /etc/wifi/wpa_supplicant.conf -B
For more detail, please refer to wpa_supplicant --help or wpa_supplicant wiki.
wpa_cli
wpa_cli is a text-based frontend program for interacting with wpa_supplicant. It is used to query current status, change configuration, trigger events, and request interactive user input.
wpa_cli can show the current authentication status, selected security mode, dot11 and dot1x MIBs, etc. In addition, it can configure some variables like EAPOL state machine parameters and trigger events like reassociation and IEEE 802.1X logoff/logon. wpa_cli provides a user interface to request authentication information, like username and password, if these are not included in the configuration. This can be used to implement, e.g., one-time-passwords or generic token card authentication where the authentication is based on a challenge-response that uses an external device for generating the response.
The control interface of wpa_supplicant can be configured to allow non-root user access (ctrl_interface GROUP = parameter in the configuration file). This makes it possible to run wpa_cli with a normal user account.
wpa_cli supports two modes: interactive and command line. Both modes share the same command set and the main difference is in interactive mode providing access to unsolicited messages (event messages, username/password requests).
Interactive mode is started when wpa_cli is executed without including the command as a command line parameter. Commands are then entered on the wpa_cli prompt. In command line mode, the same commands are entered as command line arguments for wpa_cli.
For detail, please refer to wpa_cli.
scan
There is two way to scan based on STA_WLAN.
Scan with iw
Bellow command is uesd to scan on wlan0.
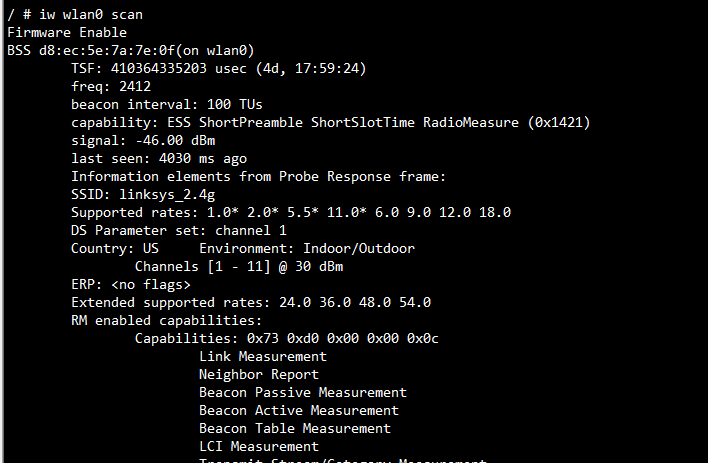
iw wlan0 scan
The following figure shows the result of above command. It prints the detail result of scanned APs.
Scan with wpa_cli
Bellow commands is uesd to scan and get scan result on wlan0.
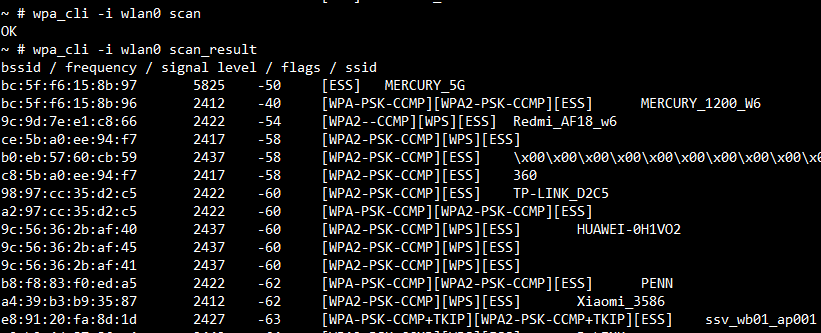
wpa_cli -i wlan0 scan
wpa_cli -i wlan0 scan_result
The following figure shows the result of above commands. It prints the detail result of scanned APs.
Set ssid and password
Bellow commands is uesd to set SSID and password on wlan0.
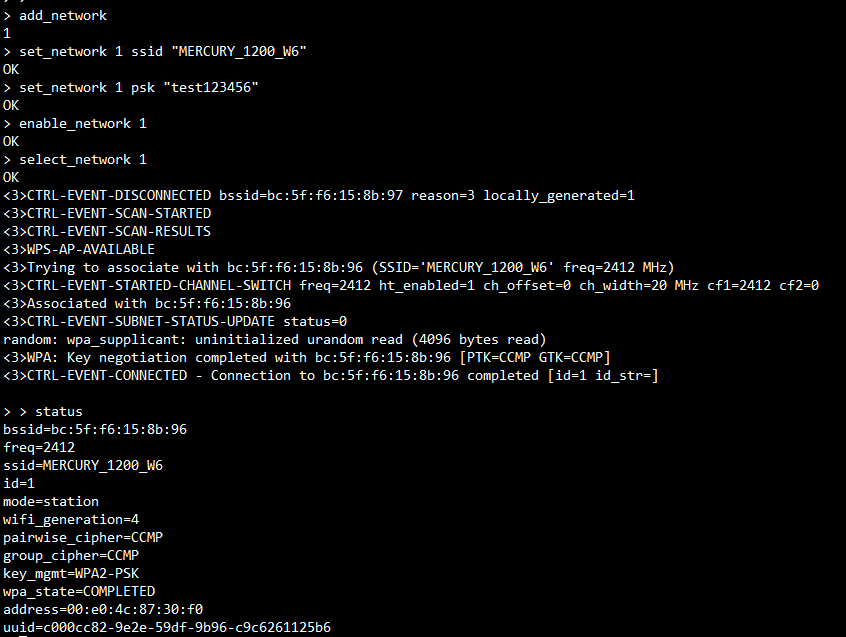
wpa_cli -i wlan0
add_network
set_network <network_id> ssid "ssid"
set_network <network_id> psk "password"
If AP is hidden AP, below command is necessary:
set_network <network_id> scan_ssid 1
Or, add scan_ssid=1 in the wpa_supplicant.conf for that hidden AP.
The following figure shows to set the SSID MERCURY_1200_W6 and password 12345678 successfully.
Note
wpa_cli -i wlan0 will enter the console of wpa_cli. All operation is running on wlan0. quit command can quit the console of wpa_cli.
Connect
Bellow commands is used to enable network and select network to connect.
enable_network <network_id>
select_network <network_id>
Note
If a network is stored in wpa_supplicant.conf, the wifi should connect the network automatically after run to wpa_supplicant.
Connect to WEP AP
wpa_supplicant
For WEP, below commands can be used to configure WEP SSID and connect the WEP AP.
# Open WEP key connection (two-message auth; no WPA, no IEEE 802.1X)
set_network id key_mgmt NONE
set_network id wep_key0 "abcde" // ASCII 64bit
set_network id wep_key1 1234567890 // hex 64bit
set_network id wep_key2 "1234567890123" // ASCII 128bit
set_network id wep_tx_keyidx 0 // key id
# Shared WEP key connection (four-message auth; no WPA, no IEEE 802.1X)
set_network id key_mgmt NONE
set_network id wep_key0 "abcde" // ASCII 64bit
set_network id wep_key1 1234567890 // hex 64bit
set_network id wep_key2 "1234567890123" // ASCII 128bit
set_network id wep_tx_keyidx 0 // key id
set_network id auth_alg SHARED
On other side, these commands can be replaced by below configuration in wpa_supplicant.conf.
# Open WEP key connection (two-message auth; no WPA, no IEEE 802.1X)
network={
ssid="static-wep-test"
key_mgmt=NONE
wep_key0="abcde" #ASCII 64bit
wep_key1=1234567890 # hex 64bit
wep_key2="1234567890123" #ASCII 128bit
wep_tx_keyidx=0 #key id
priority=5
}
# Shared WEP key connection (four-message auth; no WPA, no IEEE 802.1X)
network={
ssid="static-wep-test"
key_mgmt=NONE
wep_key0="abcde" #ASCII 64bit
wep_key1=1234567890 # hex 64bit
wep_key2="1234567890123" #ASCII 128bit
wep_tx_keyidx=0 #key id
priority=5
auth_alg=SHARED
}
iwconfig
For WEP, below commands can be used to connect the WEP AP.
iwconfig wlan0 key [id] hex //hex
iwconfig wlan0 key s:password [id] // ASCII
iwconfig wlan0 key [id] //choose psk id.
iwconfig wlan0 essid "ssid" //set ssid and connect
For more detail, please refer to iwconfig_8.
Connect with WPS
For WPS, below commands can be used when ap support and enable related capabilities.
Note
WPS doesn’t support WPA3 Wi-Fi security according to the specification.
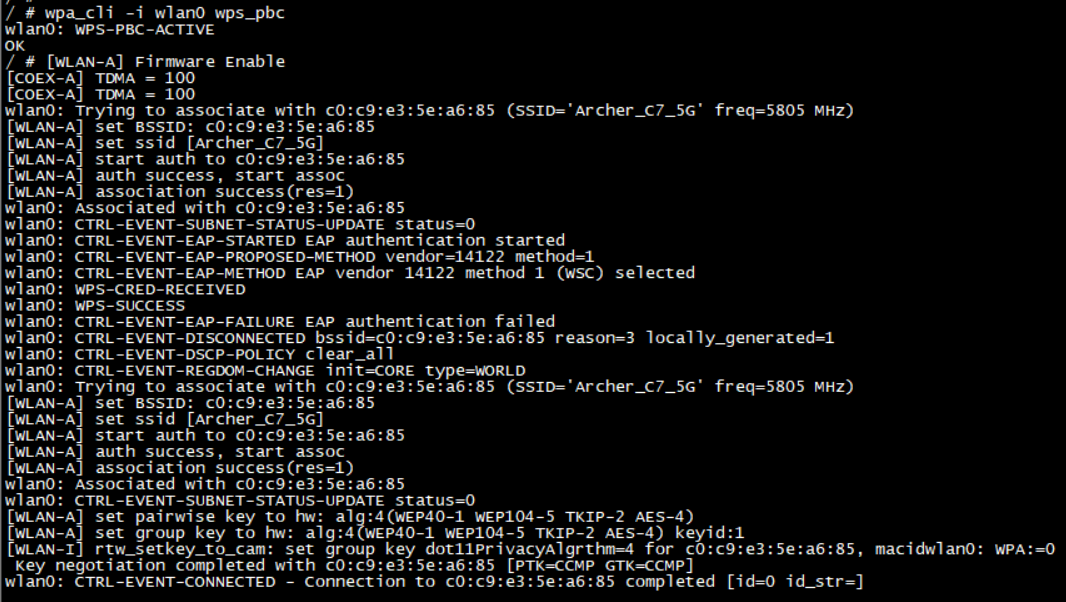
WPS PBC
Excute below command and press the Push-Button in the router in 2 min, then network configuration can be received from the ap and stored in wpa_supplicant.conf.
wpa_cli -i wlan0 wps_pbc [BSSID]
Note
It may fail when there is more than 1 client or ap in PBC state.
WPS PIN - Client pin
Excute below command, you will get a pin number or used specified pin value in this command. Input the pin number in the router and then network configuration can be received from the ap and stored in wpa_supplicant.conf.
wpa_cli -i wlan0 wps_pin <BSSID | any> [pin_number]
Note
The specified pin number used in the commands must be processed by an UI to remove non-digit characters and potentially, to verify the checksum digit. Below commands can be used to do such processing.
wpa_cli wps_check_pin <PIN>
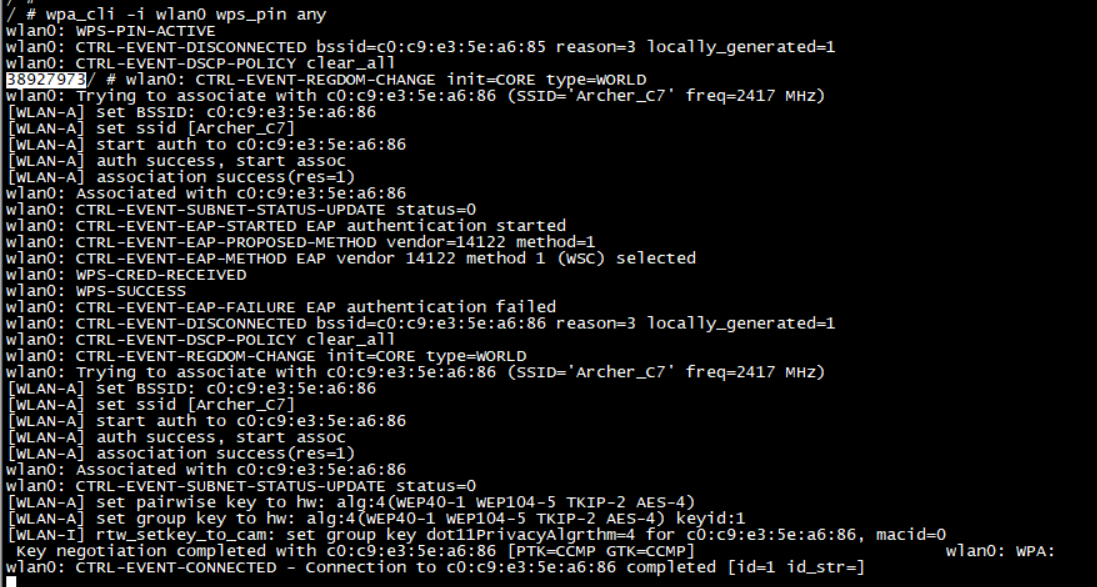
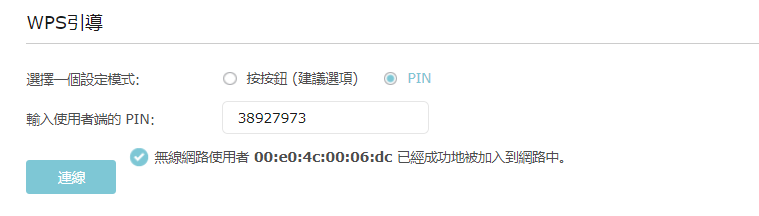
WPS PIN - Router pin
Enable router pin capability and get the bssid or the router pin value from the web_interface or the label in the router, use below command to connect ap.
wpa_cli -i wlan0 wps_reg <BSSID > <AP PIN>
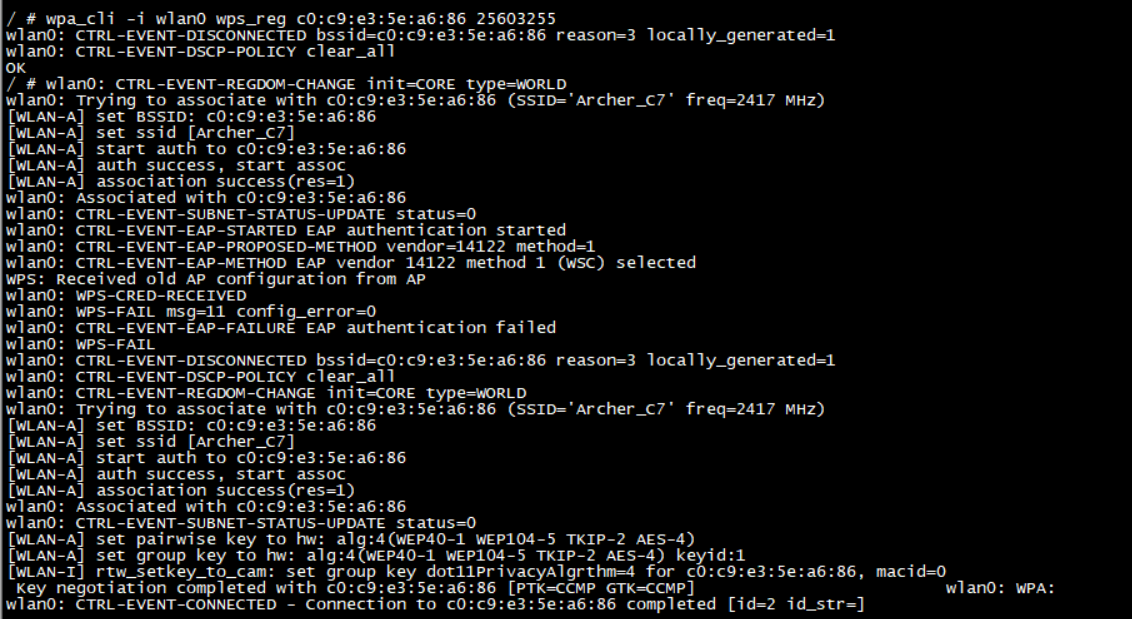
For more detail, please refer to WPS.
Disconnect and Reconnect
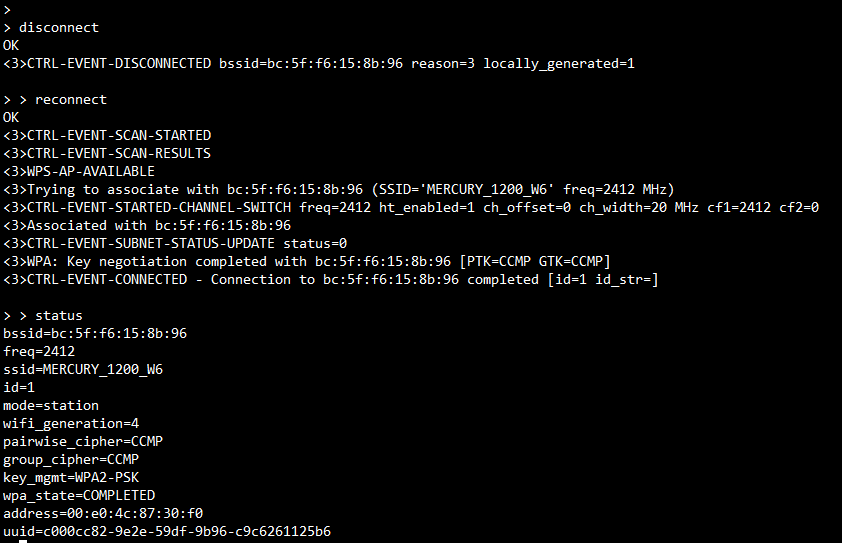
Bellow commands is used to disconnect network.
disconnect
Bellow commands is used to reconnect network.
reconnect
The following figure shows to disconnect network 1 then reconnect it is successfully.
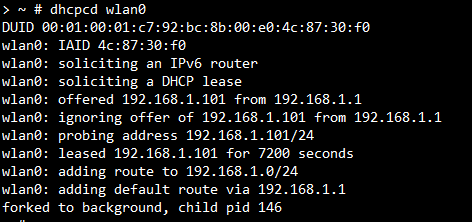
DHCP
dhcpcd wlan0 is used to get IP address from the AP’s DHCP server. The following figure shows the sample to run DHCP client and get the IP 192.168.1.101.
SoftAP mode
hostapd
hostapd (host access point daemon) is a user space daemon software enabling a network interface card to act as an access point and authentication server.
hostapd.conf
The hostapd.conf is the configuration file of hostapd and stored in /etc normally. It includes the parameters of SoftAP.
driver=nl80211
logger_syslog=-1
logger_syslog_level=2
logger_stdout=-1
logger_stdout_level=2
ctrl_interface=/var/run/hostapd
hw_mode=g
channel=1
ssid=sqb_test
beacon_int=100
dtim_period=1
max_num_sta=20
rts_threshold=2347
fragm_threshold=2346
ieee80211n=1
erp_send_reauth_start=1
wpa=2
wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
wpa_pairwise=CCMP
wpa_passphrase=12345678
Above file is an example for hostapd.conf, and it sets the SSID sqb_test and password 12345678. For more detail, please refer to hostapd wiki.
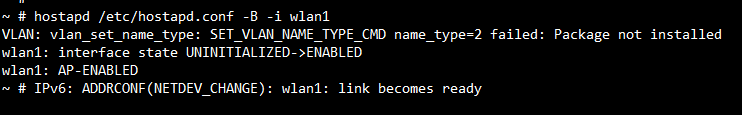
Run hostapd
Below command can run hostapd in background and start softap on wlan1.
hostapd /etc/hostapd.conf -B -i wlan1
The following figure shows to start softap successuffly.
Note
Whether wlan0 nor wlan1 can be running as softap. If one port works as softap and other works as station, the wifi is working in concurrent mode.
DHCP server
This flow is as below.
ifconfig wlan1 192.168.43.1
udhcpd -S /etc/udhcpd.conf
Test
Environment
Station Test Environment
Note
AP: a router with WiFi AP to support 11 a/b/g/n.
PC: a personal computer to connect to AP’s LAN port with Ethernet cable.
DUT: The device to test, it should be ameba smart board. It will connect to AP with wireless and connect to PC with serial port cable.
The PC can control the DUT with console of serial port cable.
Softap Test Environment
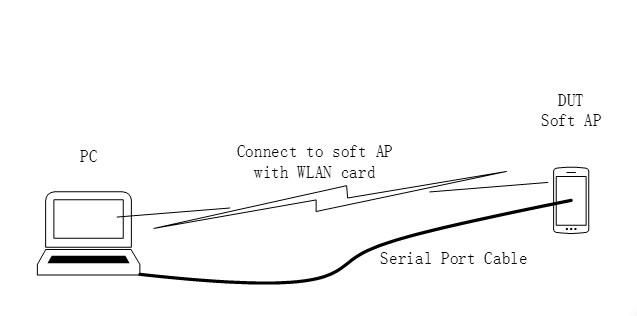
Note
PC: a personal computer with WiFi card to support 11 a/b/g/n.
DUT: The device to test, it should be ameba smart board. It will connect to PC with wireless and serial port cable.
The PC can control the DUT with console of serial port cable
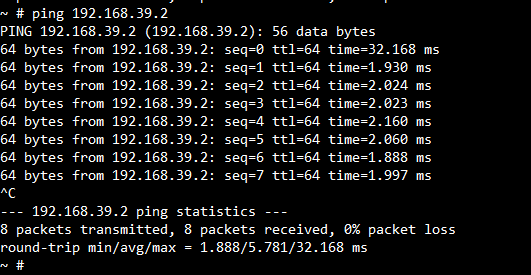
Ping Test
ping in system is classic ping tool in Linux, and ping -h can get the help information. The following figure shows to ping the 192.168.39.2 and no packet loss.
Throughput Test
This system support iperf3 to test the throughput of Wi-Fi, and iperf3 is classic in Linux. iperf3 -h can get the help information.
# To run as a server, UPD or TCP:
iperf3 -s -i 1
# To run as a client of TCP:
iperf3 -c ip_of_server -i 1 -t count
# To run as a client of UDP:
iperf3 -c ip_of_server -i 1 -t count -u -b bandwidth
Note
ip_of_server is the IP address of server.
The unit of count is second.
Bandwidth’s unit should be K, M or G. There are some errors in official windows iperf3 bin, so bandwidth should be set to the limit of real bandwidth of WiFi.
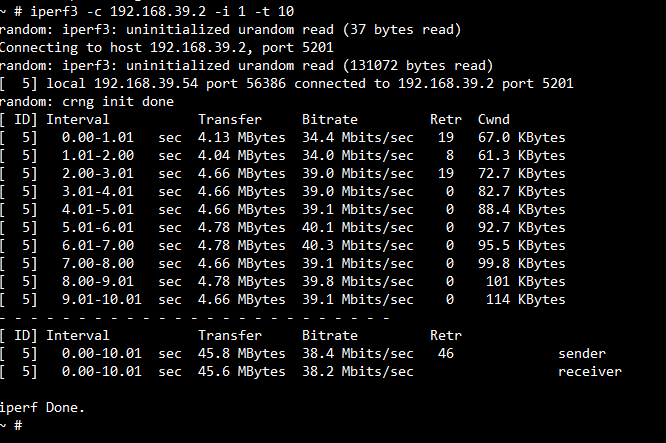
TP for TCP TX
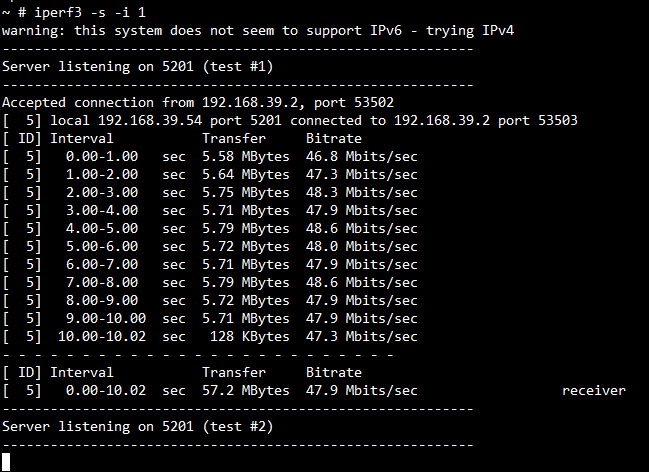
TP for TCP RX
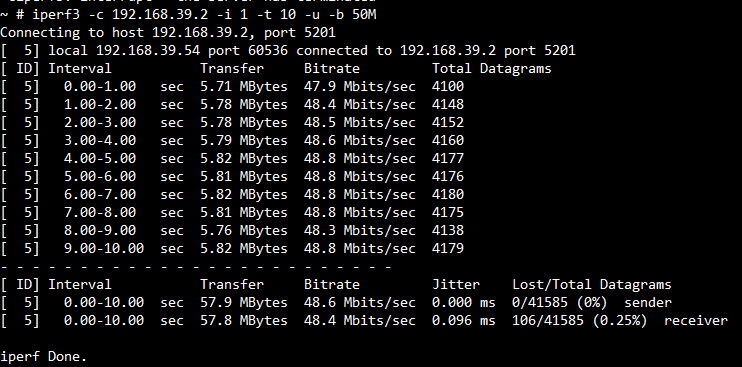
TP for UDP TX
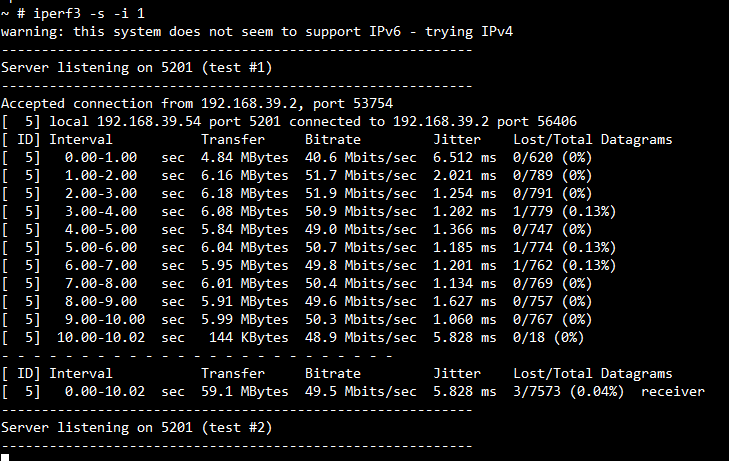
TP for UDP RX
DNS Test
Below command can add the AP_IP as the DNS server for Linux.
echo "nameserver AP_IP" >> /etc/resolv.conf
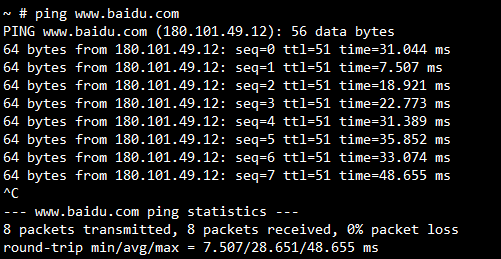
The following figure shows the result to ping www.baidu.com.
IP Forward
Below command can set the forward. The DUT connected softap can ping the AP connected by wlan0.
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o wlan0 -j MASQUERADE
Adb shell
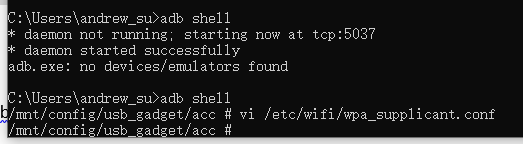
If the adb function want to be used, the usb.sh adb should be executed on the board to initialize the USB adb function. Then to enter adb shell on the PC to connect to board.
The following figure shows to enter adb shell connecting board seccussfully.
Debug
Refer to the section of Trace Tool.