Supported Chips
WHC Overview
In the WHC solution, Ameba functions as a network card connected to the host MCU via UART/SPI/SDIO/USB, providing network connectivity capabilities to the Host. The architecture diagram of WHC is shown below:
WHC Architecture Advantages
Rich interface options: Establishes transmission channels between Host and Device via UART/SPI/SDIO/USB
Cross-platform compatibility: Supports Linux, FreeRTOS, and Zephyr as Host development environments
Linux platform adaptation: Compatible with Linux standard wpa_supplicant (WPA_STD) and cfg80211 wireless frameworks, supporting enhanced features:
SME mode (with wpa_supplicant handling Wi-Fi MLME) or non-SME mode
Support for P2P/NAN
Fat Host and Slim Host
Based on whether wpa_supplicant runs on the Host side, WHC is categorized into two architectures: Fat Host and Slim Host. The Linux cfg80211 architecture belongs to the Fat Host category:
WHC Configuration Options
Selectable WPA_SUPPLICANT:
WPA_LITE: Optimized wpa_supplicant with reduced code size and memory footprint, implementing basic connectivity
WPA_STD: Standard Linux wpa_supplicant providing advanced features including P2P/NAN/SME
Selectable WPA_SUPPLICANT OFFLOAD:
WPA_SUPPLICANT can run either on Host side (e.g., Linux cfg80211) or on Device side
Running on Device side avoids porting wpa_supplicant to non-Linux host platforms, accelerating project timelines
Optional Dual TCPIP
Simultaneous operation of LWIP on Device and TCP/IP stack on Host
Device-side LWIP maintains keep-alive mechanisms, reducing Host wake-ups - ideal for battery-powered applications like IP cameras
Device-side LWIP protocol stack assists Host with packet processing, enabling traffic pre-filtering
WHC Operating Modes
Abbreviation |
wpa_supplicant |
Dual TCPIP(T) |
API PATH |
CMD PATH |
Status |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
slim host |
S1D |
WPA LITE in DEV |
N |
N |
Y |
Ready |
S1D-T |
WPA LITE in DEV |
Y |
N |
Y |
Ready |
|
fat host (cfg80211) |
S2H |
WPA STD in Host |
N |
Y |
Y |
Ready |
S2H-T |
WPA STD in Host |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Ready |
|
S2H-SME |
WPA STD in Host |
N |
Y |
Y |
Ongoing |
|
S2H-T-SME |
WPA STD in Host |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Ongoing |
Abbreviation |
wpa_supplicant |
Dual TCPIP(T) |
API PATH |
CMD PATH |
Status |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
slim host |
S1D |
WPA LITE in DEV |
N |
N |
Y |
Ready |
S1D-T |
WPA LITE in DEV |
Y |
N |
Y |
Ready |
|
fat host |
S1H |
WPA LITE in Host |
N |
Y |
Y |
Ready |
S1H-T |
WPA LITE in Host |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Ready |
Abbreviation |
wpa_supplicant |
Dual TCPIP(T) |
API PATH |
CMD PATH |
Status |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
slim host |
S1D |
WPA LITE in DEV |
N |
N |
Y |
TODO |
S1D-T |
WPA LITE in DEV |
Y |
N |
Y |
Ready |
|
fat host |
S2H |
WPA ZEPHYR in Host |
N |
Y |
Y |
TODO |
S2H-T |
WPA ZEPHYR in Host |
Y |
Y |
Y |
TODO |
Note
Abbreviations Introduction
S1 represents the Realtek-optimized wpa_supplicant: WPA_LITE
S1D indicates: wpa_supplicant using WPA_LITE and running on the Device side
S2 represents the standard wpa_supplicant: WPA_STD (supports advanced features like P2P/NAN)
S2H indicates: wpa_supplicant using WPA_STD and running on the Host side
T represents the Dual TCPIP protocol stack mode where TCPIP stacks run on both Host and Device sides
Note
MENU CONFIG
The above configuration options correspond to the following options in Menuconfig’s :
(Top) -> CONFIG WHC INTF -> FULLMAC config
----Configuration----
(X) Support WHC CMD PATH
( ) Support WHC WIFI API PATH
( ) Support WHC SUPPLICANT OFFLOAD
( ) Support WHC DUAL TCPIP
WHC Transmission Interface
Interface |
SDIO |
SPI |
USB |
UART |
SDIO (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
SPI (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
USB (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Wi-Fi |
Y |
Y |
Y |
X |
Y |
Y |
X |
BT |
Y |
Y |
X |
X |
Y |
Y |
X |
Interface |
SDIO |
SPI |
USB |
UART |
SDIO (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
SPI (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
USB (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Wi-Fi |
Y |
Y |
X |
X |
Y |
Y |
X |
BT |
Y |
Y |
X |
X |
Y |
Y |
X |
Interface |
SDIO |
SPI |
USB |
UART |
SDIO (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
SPI (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
USB (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Wi-Fi |
Y |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
BT |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
Interface |
SDIO |
SPI |
USB |
UART |
SDIO (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
SPI (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
USB (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Wi-Fi |
Y |
Y |
Y |
X |
Y |
Y |
X |
BT |
Y |
Y |
X |
X |
Y |
Y |
X |
Interface |
SDIO |
SPI |
USB |
UART |
SDIO (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
SPI (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
USB (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Wi-Fi |
Y |
Y |
X |
X |
Y |
Y |
X |
BT |
Y |
Y |
X |
X |
Y |
Y |
X |
Interface |
SDIO |
SPI |
USB |
UART |
SDIO (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
SPI (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
USB (Wi-Fi) + UART (BT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Wi-Fi |
Y |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
BT |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
WHC File TREE
Wi-Fi
├─ whc
│ ├─ README.md
│ ├─ CMakeLists.txt
│ ├─ whc_def.h
│ ├─ whc_dev
│ │ ├─ ipc
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_dev_api.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_dev_trx.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_dev_trx.h
│ │ │ └─ whc_ipc_device.c
│ │ ├─ sdio
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_dev.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_dev.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_drv.c
│ │ │ └─ whc_sdio_drv.h
│ │ ├─ spi
│ │ │ ├─ whc_spi_dev.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_spi_dev.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_spi_drv.c
│ │ │ └─ whc_spi_drv.h
│ │ ├─ usb
│ │ │ ├─ whc_usb_dev.c
│ │ │ └─ whc_usb_dev.h
│ │ ├─ whc_dev.h
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_api.c
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_api.h
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_api_path.c
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_api_path.h
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_app.c
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_cust_evt.c
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_cust_evt.h
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_msg_queue.c
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_msg_queue.h
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_protocal_offload.c
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_protocal_offload.h
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_tcpip.c
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_tcpip.h
│ │ ├─ whc_dev_trx.c
│ │ └─ whc_dev_trx.h
│ ├─ whc_host_rtos
│ │ ├─ ipc
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_host.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_host_api.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_host_api.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_host_api_basic.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_host_api_ext.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_host_trx.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_ipc_host_trx.h
│ │ │ └─ whc_ipc_host_zephyr.c
│ │ ├─ spi
│ │ │ ├─ whc_spi_host.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_spi_host.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_spi_host_trx.c
│ │ │ └─ whc_spi_host_trx.h
│ │ ├─ sdio
│ │ │ ├─ rtw_sdio_drvio.c
│ │ │ ├─ rtw_sdio_drvio.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_init.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host_trx.c
│ │ │ └─ whc_sdio_host_trx.h
│ │ ├─ whc_host.h
│ │ ├─ whc_host_api.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_api.h
│ │ ├─ whc_host_api_basic.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_api_ext.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_app.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_app.h
│ │ ├─ whc_host_init.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_cust_evt.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_cust_evt.h
│ │ └─ whc_rtos
│ │ ├─ os_wrapper_memory.c
│ │ ├─ os_wrapper_mutex.c
│ │ └─ os_wrapper_semaphore.c
│ ├─ whc_ipc.h
│ ├─ whc_ipc_cfg.h
│ ├─ whc_ipc_msg_queue.c
│ └─ whc_ipc_msg_queue.h
├─ whc_host_linux
│ ├─ Kconfig
│ ├─ Makefile
│ ├─ fullmac_setup.sh
│ ├─ app
│ │ ├─ Makefile
│ │ ├─ whc_host_app_api.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_app_api.h
│ │ └─ whc_host_app.c
│ ├─ fullmac
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_wiphy.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_regd.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_regd.h
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_protocal_offload.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_promisc.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_promisc.h
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_proc.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_proc.h
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_pkt_rx.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_ops_p2p.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_ops_nan.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_ops_key.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_ops_ap.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_ops.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_netdev_ops_p2p.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_ioctl.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_ioctl.h
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_event_tx.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_event_rx.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_cust_evt.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_cust_evt.h
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_cfgvendor.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_cfgvendor.h
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_acs.c
│ │ ├─ whc_fullmac_host_acs.h
│ │ ├─ usb
│ │ │ └─ Kbuild
│ │ ├─ spi
│ │ │ └─ Kbuild
│ │ ├─ sdio
│ │ │ └─ Kbuild
│ ├─ common
│ │ ├─ autoconf.h
│ │ ├─ whc_host_cmd_path_api.h
│ │ ├─ whc_host_cmd_path_tx.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_event.h
│ │ ├─ whc_host_hci.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_hci.h
│ │ ├─ whc_host_memory.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_netlink.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_netlink.h
│ │ ├─ whc_host_ops.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_pkt_rx.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_pkt_tx.c
│ │ ├─ whc_host_trx.h
│ │ ├─ netdev
│ │ │ ├─ whc_host_drv_probe.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_host_drv_probe.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_host_ethtool_ops.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_host_ethtool_ops.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_host_function.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_host_linux.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_host_netdev_ops.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_host_netdev_ops.h
│ │ │ └─ whc_host_wiphy.h
│ │ ├─ sdio
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host_drvio.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host_drvio.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host_fwdl.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host_init.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host_ops.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host_ops.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_sdio_host_probe.c
│ │ │ └─ whc_sdio_host_reg.h
│ │ ├─ spi
│ │ │ ├─ whc_spi_host.h
│ │ │ ├─ whc_spi_host_ops.c
│ │ │ ├─ whc_spi_host_probe.c
│ │ │ └─ spidev-overlay.dts
│ │ └─ usb
│ │ ├─ whc_usb_host.h
│ │ ├─ whc_usb_host_ops.c
│ │ └─ whc_usb_host_probe.c
WHC Hardware Configuration
Interface Connections
The pin connections between Ameba and Raspberry Pi are as follows:
Note
SPI DEV_TX_REQ: Ameba notifies Host of pending data transmission via rising edge on this pin
SPI DEV_READY: Ameba status indicator
High level (1): Device ready to receive data
Low level (0): Device busy (pause transmission)
Note
Default SDIO pins defined in Ameba SDK are used. If modification is required, adjust the SDIO_Pin_Grp parameter in the files below, which corresponds to the pinmux index in SDIO_PAD :
file location:
component/soc/usrcfg/amebadplus/ameba_intfcfg.cfile location:
component/soc/usrcfg/amebagreen2/ameba_intfcfg.cHost-side SDIO interrupt requirements:
SDIO_DATA1 must be configured for SDIO function (not GPIO).
Switch to polling mode if Host doesn’t support SDIO interrupts.
SDIO Adapter Board
Realtek provides adapter board that enables convenient connection to mini SD card slots. It is recommended to use dedicated adapter boards for interfacing with SDIO pins.
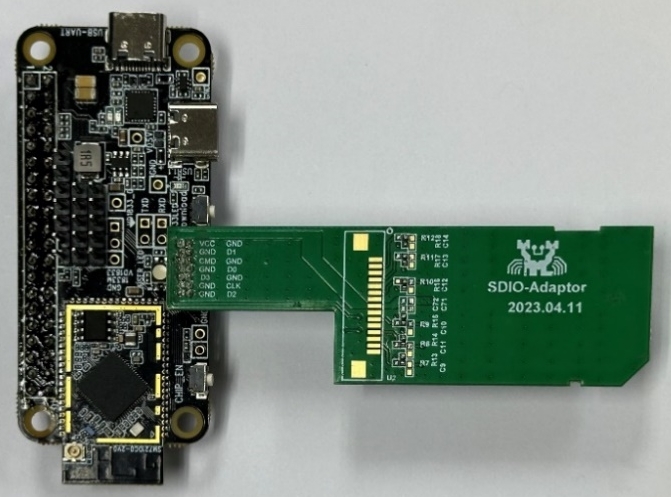
FullMAC SDIO adapter board (physical diagram)
Note
Realtek official adapter boards will be available soon. Currently request samples via <claire_wang@realsil.com.cn>.
Raspberry Pi Direct Connection
For high-speed scenarios, directly solder Ameba SDIO pins to Raspberry Pi GPIO.
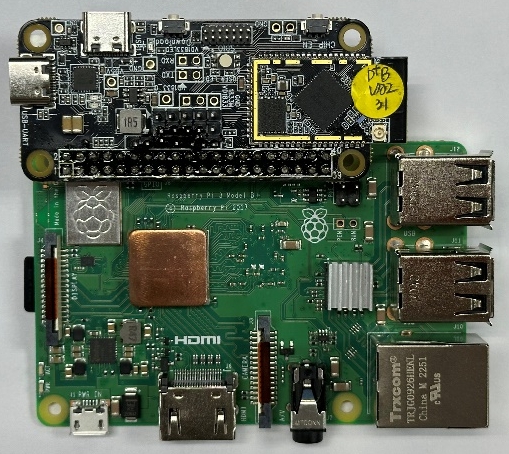
Ameba-Raspberry Pi direct connection diagram
WHC CONTROL APP
The Ameba SDK includes a Control Application to enable serial port-based device control with the following technical specifications:
Functional Purpose:Strictly for demonstration purposes, command interaction prototyping
Architecture Design:Standalone utility,non-integrated with production modules
Customization Capability:Supports code-level customization and functional extensions
Application Architecture
The application supports bidirectional communication between User Space and Kernel Space through two command types:
Kernel-Level Configuration
setmac:Configure device MAC addressnetifon:Activate network interface carrier
Device-Level Control
getmac: Retrieve device MAC addressgetip: Retrieve device IP configurationsetrdy: Notify device that host is ready and instruct device to acquire PMU_FULLMAC_WIFI lockunrdy: Notify device that host is not ready and release device’s PMU_FULLMAC_WIFI locktickps: Tickless Power Save commandwifion: Notify device to initialize WiFi
The communication architecture is shown below:
Supported Commands
Command Format |
Description |
init |
Initialize kernel Netlink communication channel |
getmac <device_idx> |
Retrieve specified device MAC address device_idx: Device port index (0 or 1 only)
|
getip <device_idx> |
Retrieve device network layer configuration device_idx: Device port index (same as getmac) |
setrdy |
Notify device host is ready and instruct acquisition of PMU_WHC_WIFI lock |
unrdy |
Notify device host is not ready and release device’s PMU_WHC_WIFI lock |
setmac <device_idx> <mac> |
Configure interface hardware address
|
netifon <device_idx> |
Activate physical layer carrier device_idx: Device port index (same as getmac) |
tickps <subtype> |
Tickless Power Save command subtype: Tickless Power Save command type
|
wifion |
Notify device to initialize WiFi |
connect <ssid> <pw> |
Notify device to connect
|
dhcp |
Notify device for IP negotiation |
Compilation and Execution
# Enter module directory
cd ${SDK}/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux/app
# Compile executable
make
# Run with privileged mode
sudo ./whc_ctrl_app
Application Architecture
The application supports controlling the Device via serial port,The communication architecture is shown below:
Supported Commands
Command Format |
Description |
whc hostrtos |
Configure Host OS mode |
whc getmac <device_idx> |
Retrieve specified device MAC address device_idx: Device port index (0 or 1 only)
|
whc getip <device_idx> |
Retrieve device network layer configuration device_idx: Device port index (same as getmac) |
whc setrdy |
Notify device host is ready and instruct acquisition of PMU_WHC_WIFI lock |
whc unrdy |
Notify device host is not ready and release device’s PMU_WHC_WIFI lock |
whc wifion |
Notify device to initialize WiFi |
whc connect <ssid> <pw> |
Notify device to connect
|
whc dhcp |
Notify device for IP negotiation |
whc scan |
Initiate network scanning on the device. |
WHC Wi-Fi Porting Guide
Device Driver Porting
In the directory {SDK}/amebadxxx_gcc_project, execute ./menuconfig.py.
Find and select .
(Top) -> CONFIG WHC INTF -> WHC_MODE ----Configuration---- ( ) WHC_IPC (X) FULLMAC_DEV ( ) FULLMAC_HOST
Find and select the desired interface, such as .
(Top) -> CONFIG WHC INTF -> HW INTERFACE ----Configuration---- (X) WHC_INTF_SDIO ( ) WHC_INTF_USB ( ) WHC_INTF_SPI
Find and select the desired module.
(Top) -> CONFIG WHC INTF -> FULLMAC config ----Configuration---- ( ) Support WHC CMD PATH ( ) Support WHC WIFI API PATH ( ) Support WHC SUPPLICANT OFFLOAD ( ) Support WHC DUAL TCPIP
If you want to enable Wi-Fi NAN or Wi-Fi P2P, locate , and select the desired feature:
(Top) -> CONFIG WIFI ----Configuration---- (X)ENABLE WIFI ---> CONFIG WIFI MODE ---> (X) ENABLE NAN ( ) ENABLE P2P
Execute
./build.pyto generatekm4_boot_all.binandkm0_km4_app.bin.Use the image tool to download the firmware to the development board.
Host Driver Porting
User Guide for Ameba as FullMAC Host
Environment Setup
Execute the configuration tool in the directory
{SDK}/amebadplus_gcc_project(Top) -> CONFIG WHC INTF -> WHC_MODE ----Configuration---- ( ) WHC_IPC ( ) FULLMAC_DEV (X) FULLMAC_HOST (Top) -> CONFIG WHC INTF -> FULLMAC HOST config ----Configuration---- (X) Support WHC CMD PATH (X) Support WHC WIFI API PATH
Firmware Compilation
Generate target files:
./build.py
Output files:
km4_boot_all.binkm0_km4_app.bin
Firmware Burning
Use the dedicated burning tool to write the firmware to the development board
Third-party Platform Porting
When using other Host chips, the component/os/freertos directory must be ported to the target system.
FullMAC is currently tested and validated on Linux kernels 5.4 and 5.10. If you encounter compilation issues on other kernel versions, contact <claire_wang@realsil.com.cn>.
Note
SPI initiates data transfer immediately after CS pin is pulled low and CLK is detected. Corner cases may occur during bus busy states.
Testing shows adding a 7μs delay between CS low and host CLK push ensures safe data transmission.
However, older SPI drivers without spi_delay support may require direct code modification.
Prerequisites
Install dependencies on Linux:
sudo apt-get install build-essential
sudo apt install dhcpcd hostapd dhcpd
Interface Activation
Linux PC: Skip this step
Raspberry Pi:
Configure SDIO via
dtoverlay.For Raspberry Pi 4:
sudo dtoverlay sdio poll_once=off
Driver Compilation
In directory
/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux, run the following cmd.nanandp2pis an optional parameter and should be added only when Wi-Fi NAN and Wi-Fi P2P needs to be enabled.
./fullmac_setup.sh sdio [nan] [p2p]
./fullmac_setup.sh spi [nan] [p2p]
./fullmac_setup.sh usb [nan] [p2p]
Copy
whc_host_linuxto Linux kernel source treeOpen new terminal and compile
cd {driver_path}/whc_host_linux make
Driver Loading
Module Path:
/whc_host_linux/sdio/fullmac_sdio.kosudo su cp sdio/fullmac_sdio.ko /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/ depmod -a modprobe fullmac_sdio
Module Path:
/whc_host_linux/spi/fullmac_spi.kosudo su cp spi/fullmac_spi.ko /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/ depmod -a modprobe fullmac_spi
Module Path:
/whc_host_linux/usb/fullmac_usb.kosudo su cp usb/fullmac_usb.ko /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/ depmod -a modprobe fullmac_usb
After successful loading, run
ifconfigto verify Wi-Fi devices.Sample Output:
Station mode MAC prefix:
00:e0:4cSoftAP mode MAC prefix:
00:e1:4c
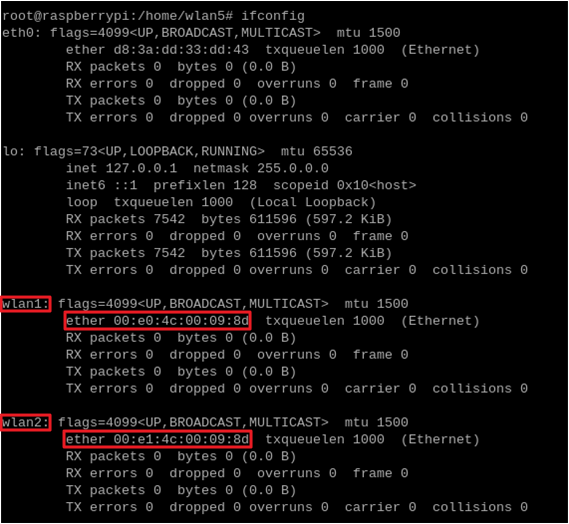
WHC Demonstration
Initial Configuration
Run the Control Application
cd ${SDK}/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux/app sudo ./whc_ctrl_app
Execute initialization sequence in Control App
> init > wifion > getmac 0 00:0A:35:XX:XX:XX > setmac 0 00:0A:35:11:22:33
Connect to Wireless Network
Perform WiFi scan in control app
> scan
Establish wireless connection in control app
> netifon 0 > connect ap_test 12345678Note
ap_testrepresents the target AP’s SSID,12345678is the target AP’s password. Omit password parameter for open networks.
Configure network interface in a new terminal
> dhcpcd wlanXNote
wlanXis the interface device name. Confirm actual interface name (e.g., wlan0/wlan1) usingifconfig -a
Network Testing
ping 192.168.x.x
Initial Configuration
Run the Control Application
cd ${SDK}/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux/app sudo ./whc_ctrl_app
Execute initialization sequence in Control App
> init > wifion > getmac 0 00:0A:35:XX:XX:XX > setmac 0 00:0A:35:11:22:33
Connect to Wireless Network
Perform WiFi scan in control app
> scan
Establish wireless connection in control app
> netifon 0 > connect ap_test 12345678Note
ap_testrepresents the target AP’s SSID,12345678is the target AP’s password. Omit password parameter for open networks.
Retrieve IP configuration from device
> getip 0
Configure host network interface
sudo ip addr add 192.168.x.x/24 dev wlanX sudo ip link set wlanX up sudo ip route add default via 192.168.x.x dev wlanXNote
Verify interface name using
ip link showorifconfig(Actual name may differ from wlanX, e.g., wlan0)
Validate interface status
> netifon 0
Network Validation
ping 192.168.x.x
Driver Loading Verification
Connecting to Wireless Network
Note
Ubuntu System Note: When connecting via command line, stop NetworkManager and DHCP services to avoid conflicts.
sudo systemctl stop NetworkManager dhcpcd.service sudo systemctl disable NetworkManager
Create configuration file
/etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.confctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant network={ ssid="HUAWEI-JX2UX5_HiLink_5G" psk="12345678" }
Start WPA connection
wpa_supplicant -D nl80211 -i wlanX -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf -dd > /var/wifi_logNote
wlanXis the interface device name. Confirm actual interface name (e.g., wlan0/wlan1) usingifconfig -a
Obtain IP address
dhcpcd wlanX
Configuring SoftAP
Create configuration file
/etc/hostapd/hostapd.confdriver=nl80211 logger_syslog=-1 logger_syslog_level=2 hw_mode=g channel=6 ssid=aaa_test wpa=2 wpa_passphrase=12345678 wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK wpa_pairwise=CCMP
Create DHCP configuration file
/etc/udhcpd_wlanX.confstart 192.168.43.20 end 192.168.43.254 interface wlanX opt dns 192.168.43.1 option subnet 255.255.255.0 opt router 192.168.43.1
Start SoftAP
hostapd /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf -i wlanX
Set AP IP address
ifconfig wlanX 192.168.43.1
Start DHCP service
udhcpd -f /etc/udhcpd_wlanX.conf
Driver Loading Verification
Connecting to Wireless Network
Note
Ubuntu System Note: When connecting via command line, stop NetworkManager and DHCP services to avoid conflicts.
sudo systemctl stop NetworkManager dhcpcd.service sudo systemctl disable NetworkManager
Create configuration file
/etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.confctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicant network={ ssid="HUAWEI-JX2UX5_HiLink_5G" psk="12345678" }
Start WPA connection
wpa_supplicant -D nl80211 -i wlanX -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf -dd > /var/wifi_logNote
wlanXis the interface device name. Confirm actual interface name (e.g., wlan0/wlan1) usingifconfig -a
Obtaining IP Address
Launch Control Application
cd ${SDK}/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux/app sudo ./whc_ctrl_app
Execute initialization
> init
Trigger IP address acquisition
> dhcp
Configure host network settings
sudo ip addr add 192.168.x.x/24 dev wlanX sudo ip link set wlanX up sudo ip route add default via 192.168.x.x dev wlanXNote
wlanXis the interface name, obtainable by executingifconfigin terminal.
Network Testing
ping 192.168.x.x
Initial Configuration
Execute initialization sequence in Control App
> BRIDGE sethost > BRIDGE wifion > BRIDGE getmac
Connect to Wireless Network
Perform WiFi scan in control app
> BRIDGE scan
Establish wireless connection in control app
> BRIDGE connect ap_test 12345678Note
ap_testrepresents the target AP’s SSID,12345678is the target AP’s password. Omit password parameter for open networks.
Network Testing
AT+WLPING=192.168.x.x
Connect to Wireless Network
Perform WiFi scan
> AT+WLSCAN
Establish wireless connection in
> AT+WLCONN=ssid,ap_test,pw,12345678Note
ap_testrepresents the target AP’s SSID,12345678is the target AP’s password. Omit password parameter for open networks.
Network Testing
AT+WLPING=192.168.x.x
WHC Low Power Management
Device Side Operations
Configure low-power mode:
AT+TICKPS=TYPE,CG.
Host Side Operations
Identify wireless physical interface(find “phy” field):
rfkill list.Enable any-packet wakeup:
sudo iw phy <phyname> wowlan enable any(replace actual phyname).Verify WoWLAN configuration:
sudo iw phy wowlan show.Initiate system suspend
echo mem | sudo tee /sys/power/state.
Note
phyname may change to phy1/phyN after rmmod, Re-validate steps 1-3 after module reload.
WHC API
Header Files
whc_host_linux/common/whc_host_cmd_path_api.h
whc_host_linux/app/whc_host_app_api.h
component/wifi/whc/whc_host_rtos/whc_host_app.h
component/wifi/whc/whc_dev/whc_dev_api.h
Interface Definitions
int whc_host_buf_rx_to_user(u8 *buf, u16 size);
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
Function Function |
Processes device-to-host packet transmission, default forwards to user space |
Parameters |
buf: Packet buffer pointer, size: Valid packet length (bytes) |
Return |
0 indicates success, non-zero for error codes |
Note
This is a weak symbol interface in RTK SDK, recommended to override per use case.
void whc_host_send_data_to_dev(u8 *pbuf, u32 len, u32 with_txdesc);
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
Function |
Kernel-space to device packet transmission interface |
Parameters |
pbuf: Tx buffer, len: Valid data length with_txdesc: 1 indicates buffer contains TX descriptor header |
Return |
void |
int whc_host_api_send_nl_data(uint8_t *buf, uint32_t buf_len);
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
Function |
User-space to device Netlink data transmission interface |
Parameters |
buf: Structured data buffer, buf_len: Data length |
Return |
0 indicates success, non-zero for error codes |
void whc_host_pkt_rx_to_user(u8 *payload, u32 len);
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
Function |
Device-to-host application packet distribution interface |
Parameters |
payload: Data payload pointer, len: Data length |
Return |
void |
Note
This is a weak symbol interface in RTK SDK, recommended to override per use case.
void whc_host_send_to_dev(u8 *buf, u32 len);
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
Function |
Application-layer to device data transmission interface |
Parameters |
buf: Transmission buffer, len: Data length |
Return |
void |
void whc_dev_api_send_to_host(u8 *buf, u32 len);
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
Function |
Device-to-host packet transmission interface |
Parameters |
buf: Data buffer pointer, len: Valid data length |
Return |
void |
void whc_dev_pkt_rx_to_user(u8 *rxbuf, u8 *real_buf, u16 size);
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
Function |
Processes received user packets from device and delivers to device-side application |
Parameters |
rxbuf: Pointer to received data payload real_buf: Memory address for final packet deallocation size: Packet length (in bytes) |
Return |
void |
Note
This is a weak symbol interface in RTK SDK, recommended to override per use case.
WHC Wi-Fi Throughput
Interface |
Wi-Fi driver location |
Item |
Slim Host |
Fat Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SDIO [1] |
KM4 (334MHz) |
TCP RX |
49.7 |
53.5 |
TCP TX |
50.1 |
51.2 |
||
UDP RX |
58.9 |
59.6 |
||
UDP TX |
56.5 |
56.6 |
||
SPI [2] |
KM4 (334MHz) |
TCP RX |
16.8 |
17.1 |
TCP TX |
17.4 |
17.7 |
||
UDP RX |
19.1 |
18.6 |
||
UDP TX |
18.9 |
18.4 |
||
USB [3] |
TCP RX |
|||
TCP TX |
||||
UDP RX |
||||
UDP TX |
[1] The data is the test result of device code running in Flash, host:Raspberry Pi 5 Model B Rev 1.1,root: Linux raspberrypi 6.6.31+rpt-rpi-2712
[2] The data is the test result of device code running in Flash, host:Raspberry Pi 5 Model B Rev 1.0,root: Linux raspberrypi 6.6.31+rpt-rpi-2712
Interface |
Wi-Fi driver location |
Item |
Slim Host |
Fat Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SPI [1] |
KM4 (334MHz) |
TCP RX |
10.9 |
11 |
TCP TX |
10.4 |
10.6 |
||
UDP RX |
16.3 |
15.5 |
||
UDP TX |
17.1 |
17.4 |
[1] The data is the test result of device code running in Flash,host:Ameba RTL8721Dx, SPI Clk 25M
Interface |
Wi-Fi driver location |
Item |
Slim Host |
Fat Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SDIO [1] |
KM4 (320MHz) |
TCP RX |
65 |
65.5 |
TCP TX |
73.1 |
74.3 |
||
UDP RX |
81.9 |
83.8 |
||
UDP TX |
86.3 |
88 |
||
SPI [2] |
KM4 (333MHz) |
TCP RX |
17.8 |
17.8 |
TCP TX |
18.4 |
18.2 |
||
UDP RX |
19.1 |
19.0 |
||
UDP TX |
19.5 |
19.3 |
||
USB [3] |
TCP RX |
|||
TCP TX |
||||
UDP RX |
||||
UDP TX |
[1] The data is the test result of device code running in Flash, host:Raspberry Pi 5 Model B Rev 1.1,root: Linux raspberrypi 6.6.31+rpt-rpi-2712
[2] The data is the test result of device code running in Flash, host:Raspberry Pi 5 Model B Rev 1.0,root: Linux raspberrypi 6.6.31+rpt-rpi-2712
Interface |
Wi-Fi driver location |
Item |
Slim Host |
Fat Host |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SPI [1] |
KM4 (333MHz) |
TCP RX |
13.1 |
13.1 |
TCP TX |
14 |
14.4 |
||
UDP RX |
19.2 |
20.1 |
||
UDP TX |
21.9 |
22.7 |
[1] The data is the test result of device code running in Flash, host:Ameba RTL8721F, SPI Clk 25M
WHC Memory Footprint
Device
Example with Wi-Fi running on KM0:
Item |
KM0 |
KM4 |
|---|---|---|
txt |
270KB |
31KB |
rodata |
51KB |
9KB |
data+bss |
17KB |
4KB |
heap |
~68KB |
~2.5KB |
Host
Host |
Item |
whc |
|---|---|---|
SPI |
txt |
4.8KB |
bss |
~3.5KB |
|
heap |
~5KB |
Host |
Item |
fullmac_xxx.ko |
|---|---|---|
SDIO |
txt |
88KB |
data |
65KB |
|
bss |
18KB |
|
SPI |
txt |
73KB |
data |
54KB |
|
bss |
18KB |
|
USB |
txt |
|
data |
||
bss |
Note
The characters before .ko are sdio, spi or usb, corresponding to different hosts.