Wi-Fi R-MESH
Overview
Wi-Fi R-Mesh is a tree-topology mesh network designed to extend Wi-Fi coverage, enabling stations far from the AP to also maintain stable network connectivity. The following is the network topology diagram:
Wi-Fi R-Mesh implements data forwarding directly at the Wi-Fi driver layer, consuming less RAM and MCU resources.
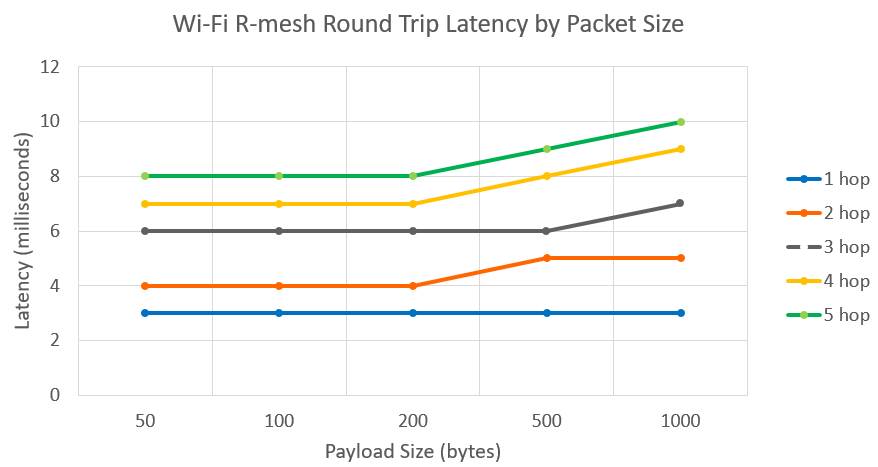
With minimal software processing required, nodes can achieve high throughput and extremely low data latency even after several hops.
Advantages
title_hide
A software-unsensible mesh network
All Mesh protocols are implemented at Wi-Fi driver layer. Both root nodes and child nodes are regarded by the application as standard Wi-Fi stations connected to the AP.
No updates are required for Wi-Fi configuration programs.
Rapid pairing and switching within microseconds
Child nodes can rapidly switch to a new parent node with better signal quality without interrupting data communication.
If the parent node encounters a problem (such as power off or hang), the child node can rapidly detect the issue and switch to an alternative parent node without interrupting data communication.
A node can migrate all its child nodes together to a new parent node while maintaining uninterrupted data flow.
High throughput and low data latency
R-Mesh forwarding bypasses the TCP/IP protocol stack, implemented directly at the driver layer, thereby consuming less RAM and MCU resources.
With extremely short software processing time, better throughput and low data latency can be achieved even after several hops.
Network stability
Simplified software architecture eliminates complex routing table algorithms, ensuring network stability.
Traditional mesh network issues like loops do not occur.