Wi-Fi Aware (NAN)
支持的芯片[ RTL8730E ][ RTL8721Dx ][ RTL8721F ]
备注
Realtek Wi-Fi NAN 功能只支持带有 wpa_supplicant 的 Linux Host, 包括 Wi-Fi 网卡模式中的 Fat Host (WHC Wi-Fi 配置选项及典型模式) 和 RTL8730E Linux 架构。
Wi-Fi NAN 概述
Wi-Fi Aware,也称为 NAN (Neighbor Awareness Networking) 协议,是一项由 Wi-Fi 联盟认证的技术标准。 它允许支持该功能的设备在不依赖于传统的网络基础设施、互联网连接或 GPS 信号的情况下,快速发现、连接并与其他 Wi-Fi 设备交换数据。 与传统的 Wi-Fi 直连(Wi-Fi Direct)相比,NAN 在设备发现阶段功耗更低、效率更高,适合需要持续感知周围环境的应用场景。 这使得一系列创新的点对点(P2P)应用成为可能,例如:
社交应用:查找附近有共同兴趣的朋友或加入一个本地游戏。
信息共享:在会议室里快速分享文件给所有与会者。
本地服务:在商场里接收附近商家的优惠券,或在博物馆里获取关于展品的详细介绍。
Wi-Fi NAN 的高效与低功耗特性,得益于其独特的工作机制,主要包括 NAN 集群、服务发布/订阅模型以及数据链路的建立。
NAN 集群
多个邻近的 NAN 设备可以自动组成一个 NAN 集群 (NAN Cluster) ,集群中的设备能够相互通信。在集群内部,设备共享一套共同的时间信标以进行同步。
设备不会一直保持唤醒状态,而是遵循一个严格的同步时钟,仅在被称为发现窗口 (Discovery Window, DW) 的极短时间片内被唤醒。 在 DW 期间,设备可以广播自己的服务或侦听来自其他设备的服务。在其余绝大部分时间里,设备都处于低功耗的休眠状态。 这种同步休眠/唤醒机制是 NAN 实现低功耗的关键,它避免了传统 Wi-Fi 为了发现彼此而需要持续扫描所带来的较大电量消耗。
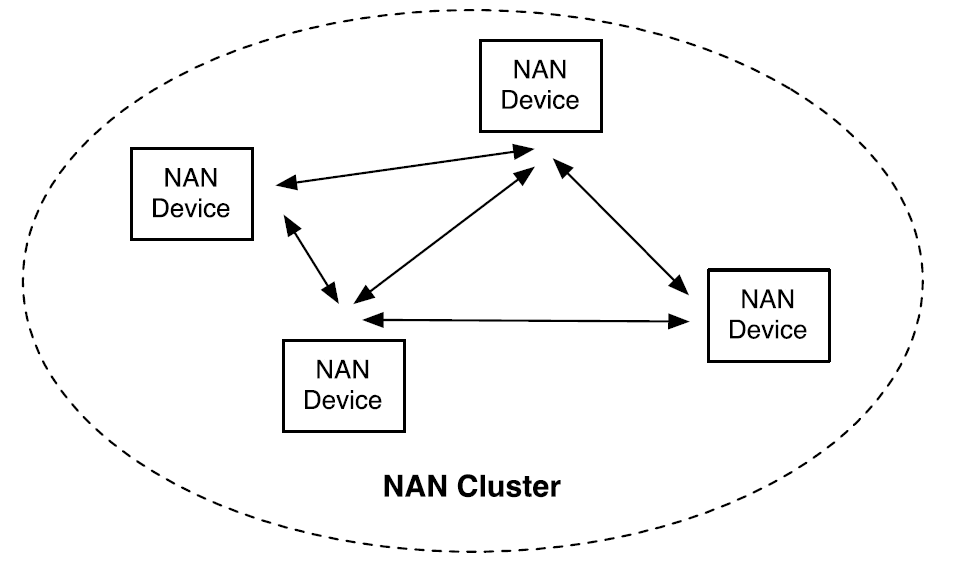
Wi-Fi NAN 集群
服务发布/订阅模型
Wi-Fi NAN 采用了一种高效的发布/订阅 (Publish/Subscribe) 模型进行服务发现:
发布服务 (Publish): 设备可以作为发布者向集群广播它所能提供的服务。
订阅服务 (Subscribe): 其他设备(订阅者)则侦听它们感兴趣的特定服务。
服务发现 (Discovery): 当订阅者在发现窗口期间侦听到匹配其订阅请求的发布消息时,则成功订阅服务。
建立数据链路 (NAN Data Path)
一旦服务订阅成功,两个设备之间就可以选择建立一个 NAN 数据链路 (NAN Data Path, NDP)。这是一个基于 Wi-Fi 的点对点直连链路,具有以下特点:
高带宽: 利用 Wi-Fi 的高速率进行数据传输。
低延迟: 直接连接,无需通过 AP 中转。
安全性: 可以使用 WPA2 安全标准对数据链路进行加密。
NDP 建立后,设备就可以进行文件传输、视频串流、实时游戏等需要高带宽和低延迟的交互。
参考资料
Wi-Fi NAN 特性支持
Realtek 设备对 Wi-Fi NAN 协议提供了全面的支持,能够作为 NAN 网络中的任何角色运行。具体支持能力如下:
核心功能支持
创建 NAN 集群: 当周围没有可用的 NAN 网络时,设备能够主动初始化一个新的 NAN 集群,并承担主节点 (Master) 的角色,负责广播同步信标,为其他设备的加入提供基础。
加入 NAN 集群: 设备能够自动扫描并发现附近已经存在的 NAN 集群,并与之同步时钟,无缝融入现有的邻近感知网络中,与其他设备进行服务发现。
发布服务: 设备可以广播(发布)一个或多个服务,让周边设备发现。
订阅服务: 设备可以订阅(搜索)特定的服务,并发现提供这些服务的设备。
建立数据链路: 设备间可以建立开放或加密的 NAN 数据链路,并协商时间窗口以进行点对点数据交换。
NAN 安全性支持
支持设备间建立加密的数据路径。基于 WPA2 AES 加密方式对单播数据帧进行保护。
支持 NAN 配对 (NAN Pairing) 进行设备间安全身份认证、密钥协商、分发与管理。
支持使用 PTK 进行单播管理帧保护。
支持使用 GTK 进行多播数据帧保护,使用 IGTK 进行多播管理帧保护。
支持使用 BIGTK 进行信标帧保护 (Beacon Protection)。
主要特性
高带宽、低延迟的数据传输: 基于 Wi-Fi 技术,确保数据交换的性能。
安全连接: 在 Wi-Fi 层对已配对设备间的连接进行认证与加密。
多连接能力:支持与多个 Wi-Fi NAN 设备同时建立连接。
网络并发:支持 Wi-Fi NAN 功能与传统 Wi-Fi 网络(STA 模式)并发使用,互不影响。
稳健的拓扑结构:采用完全的点对点拓扑,单个节点的加入或离开不会中断其他节点间的现有连接。
Wi-Fi NAN 移植指南
Realtek Wi-Fi NAN 功能支持 Linux Host, Wi-Fi 网卡模式 S2H (WHC Wi-Fi 配置选项及典型模式), 或 RTL8730E Linux。
在目录
{SDK}中执行source envsetup.sh设置编译环境。选择编译的目标 machine 和目标 distro,比如 rtl8730elh-va7-full。
You're building on Linux Lunch menu... pick a combo: 1. rtl8730elh-va7-full 2. rtl8730elh-va7-generic 3. rtl8730elh-va8-full 4. rtl8730elh-va8-generic Which would you like?进入到 build 目录后执行
mfw menuconfig。找到 ,选择 。
(Top) -> CONFIG WIFI ----Configuration---- (X)ENABLE WIFI ---> ... (X) ENABLE NAN ( ) ENABLE P2P
打开
{SDK}/sources/firmware/component/wifi/whc/whc_host_linux/Makefile,打开 NAN 的编译选项。export CONFIG_NAN = y export CONFIG_P2P = n export CONFIG_MCC = n export CONFIG_BT_INIC = n export CONFIG_FULLMAC_HCI_IPC = y
执行
m和mfw生成固件,生成位置:{SDK}/images。使用 image tool 下载固件到开发板。
Wi-Fi NAN 使用指南
Realtek NAN Utility 是一款用户空间工具,它基于开源 iw 库和 nan_vendor_wrapper 私有库,提供了 nan_test 测试脚本,可以直观便捷地操作 Wi-Fi NAN。
NAN Utility 架构如下图所示:
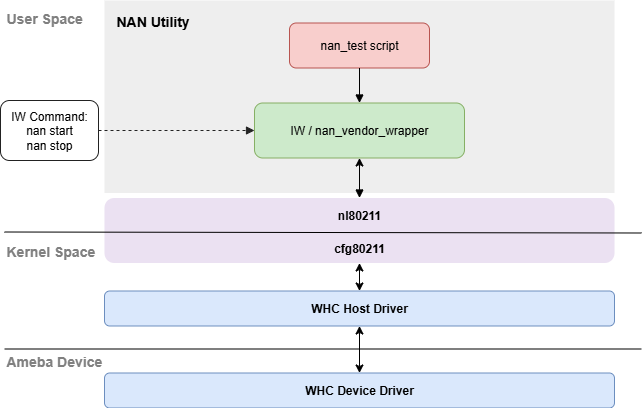
Wi-Fi NAN Utility 架构
NAN Utility 获取及编译
获取 NAN Utility
SDK 下载: IoT SDK NAN Utility 工具位于:
{sdk}/component/wifi/linux_app/nan_utility.环境准备
在 Linux 系统安装以下依赖包:
sudo apt-get install build-essential
执行编译
将
nan_utility目录复制到 Host Linux 内核源码树,终端执行编译:cd nan_utility make script
编译完成后,可执行脚本
nan_test位于nan_utility/script/路径下。
获取 NAN Utility
SDK 下载: IoT SDK NAN Utility 工具位于:
{sdk}/component/wifi/linux_app/nan_utility.环境准备
在 Linux 系统安装以下依赖包:
sudo apt-get install build-essential
执行编译
将
nan_utility目录复制到 Host Linux 内核源码树,终端执行编译:cd nan_utility make script
编译完成后,可执行脚本
nan_test位于nan_utility/script/路径下。
获取 NAN Utility
SDK 下载: Linux SDK
NAN Utility 工具位于:
{sdk}/sources/test/nan/.环境准备
编辑
{sdk}/sources/yocto/meta-realtek/meta-sdk/recipes-core/images/ameba-image-core.bb,在 IMAGE_INSTALL 中新增net-tools和iproute2库,如下:IMAGE_INSTALL += " \ net-tools \ iproute2 \ adbd \ recoveryd \
重新编译固件,并烧录固件到开发板。
执行编译
使用
bitbake指令对 NAN Utility 进行交叉编译:bitbake rtk-app-nan-test -c cleanall bitbake rtk-app-nan-test
编译产生的可执行文件位于
{sdk}/sources/tests/nan/oe-workdir/image/bin/路径下。 将该路径下的文件复制到连接开发板的 PC 上。通过 PC 上的 TraceTool 工具,在开发板上执行
usb.sh -r usbd_adb指令初始化 USB adb 功能。在 PC 上打开命令行工具,进入 NAN Utility 可执行文件所在目录,通过
adb指令将文件 push 到开发板:adb push nan_test /usr/sbin/ adb push nan_vendor_wrapper /usr/sbin
在开发板上执行指令给 NAN 测试脚本添加可执行权限:
chmod +x /usr/sbin/nan_test chmod +x /usr/sbin/nan_vendor_wrapper
NAN 应用示例
在 NAN 设备间建立 Data Path,需准备两套设备,并完成 NAN 移植以及 NAN Utility 的移植。
备注
在执行示例中的命令时,需要将其中的 MAC 地址替换为您设备的实际 NAN MAC 地址。 可在设备启动 NAN 后,通过 ifconfig 指令查看 nan0 端口的地址信息,如下:
root@raspberrypi:/# ifconfig
nan0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet6 fe80::2e2:4cff:fe00:102d prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:e2:4c:00:10:2d txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 6 bytes 516 (516.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Case 1 - Open NDP 建立
Open NDP 允许设备之间建立直接的数据通道,但不进行加密或认证,适用于对安全性要求不高的场景,具有更低的延迟和更简单的设置过程,建立流程如下图所示:
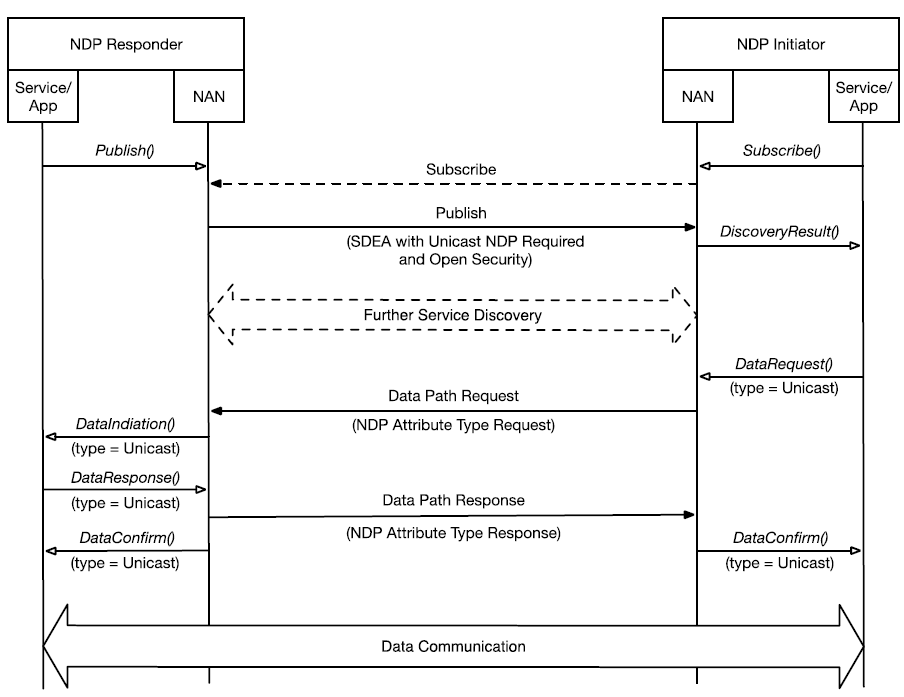
Wi-Fi NAN Open NDP 建立流程
按下表所示,在对应的 Host 终端执行指令以建立 Open NDP:
Step |
Device A(NDP Responder) MAC: 00:11:22:33:44:55 |
Device B(NDP Initiator) MAC: 66:55:44:33:22:11 |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
nan_test init nan_test start pref 128 bands 2GHz 5GHz |
Device A 初始化 NAN,并在 2G 和 5G 启动 NAN。 |
|
2 |
nan_test init nan_test start pref 5 bands 2GHz 5GHz |
Device B 初始化 NAN,并在 2G 和 5G 启动 NAN。 |
|
3 |
nan_test add_func type publish unsolicited name nanservice data_path |
Device A 发布一个未加密的服务。 |
|
4 |
nan_test add_func type subscribe name nanservice |
Device B 订阅该服务。 |
|
5 |
nan_test data_req req_type ndp rsp_nan_mac 00:11:22:33:44:55 publish_id 1 |
Device B 向 Device A 发送 Data Path Request,请求建立NDP。 |
|
6 |
nan_test data_rsp rsp_mode peer ndl_rsp accept data_path_id 1 |
Device A 回复 Data path Response,接受 NDP 请求,NDP 建立成功。 |
|
7 |
nan_test set_ipv6 nan_test set_neigh 66:55:44:33:22:11 |
nan_test set_ipv6 nan_test set_neigh 00:11:22:33:44:55 |
Device A & B 设置自身的 IPv6 地址,并将对方的 IPv6 地址添加到 IP 邻居表中。 |
8 |
ping6 fe80::6655:44ff:fe33:2211%nan0 |
Device A 通过 IPv6 地址 ping Device B,可以成功通信。 |
|
9 |
ping6 fe80::0011:22ff:fe33:4455%nan0 |
Device B 通过 IPv6 地址 ping Device A,可以成功通信。 |
Case 2 - Secure NDP 建立
Secure NDP 在设备之间建立加密的数据通道,提供了数据传输的机密性和完整性保护,建立流程如下图所示:
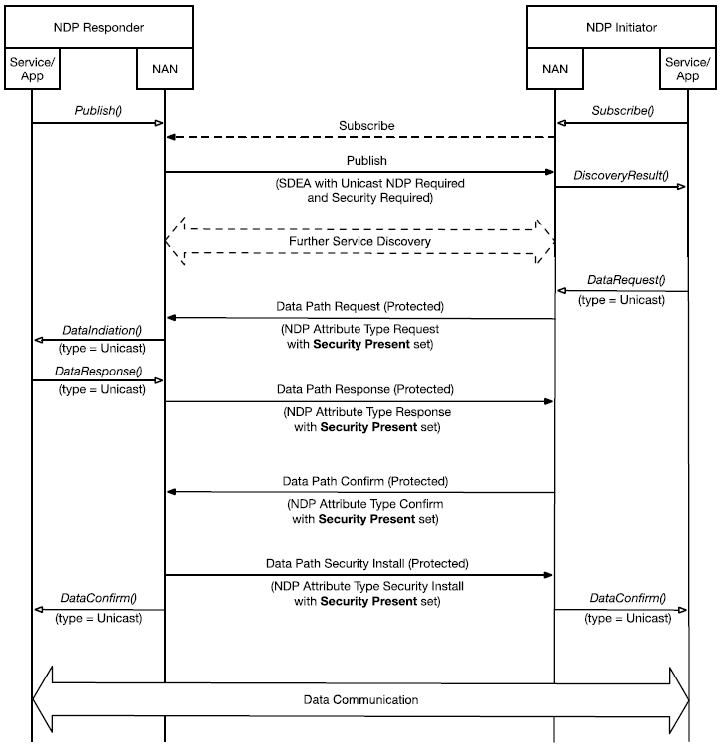
Wi-Fi NAN Secure NDP 建立流程
按下表所示,在对应的 Host 终端执行指令以建立基于 PMK 的 Secure NDP:
Step |
Device A(NDP Responder) MAC: 00:11:22:33:44:55 |
Device B(NDP Initiator) MAC: 66:55:44:33:22:11 |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
nan_test init nan_test start pref 128 bands 2GHz 5GHz |
Device A 初始化 NAN,并在 2G 和 5G 启动 NAN。 |
|
2 |
nan_test init nan_test start pref 5 bands 2GHz 5GHz |
Device B 初始化 NAN,并在 2G 和 5G 启动 NAN。 |
|
3 |
nan_test add_func type publish unsolicited name nanservice data_path sec_pmk 123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0 |
Device A 发布服务,宣称支持 ND-TKSA (SDEA with Unicast NDP required and Security Required)。 |
|
4 |
nan_test add_func type subscribe name nanservice |
Device B 订阅该服务。 |
|
5 |
nan_test data_req req_type ndp rsp_nan_mac 00:11:22:33:44:55 sec publish_id 1 sec_pmk 123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0 |
Device B 向 Device A 发送 Data Path Request,携带 sec_pmk,请求建立加密NDP。 |
|
6 |
nan_test data_rsp rsp_mode peer ndl_rsp accept data_path_id 1 |
Device A 回复 Data path Response,接受 NDP 请求,NDP 建立成功。 |
|
7 |
nan_test set_ipv6 nan_test set_neigh 66:55:44:33:22:11 |
nan_test set_ipv6 nan_test set_neigh 00:11:22:33:44:55 |
Device A & B 设置自身的 IPv6 地址,并将对方的 IPv6 地址添加到 IP 邻居表中。 |
8 |
iperf -s -i 1 -V |
Device A 运行 iperf server。 |
|
9 |
iperf -c fe80::0011:22ff:fe33:4455%nan0 -i 1 -t 30 -V |
Device B 运行 iperf client,与 Device A 建立 TCP 连接。 |
nan_test 参数说明
Command parameter |
Usage |
Comment |
|---|---|---|
-h |
show help message |
|
status |
show current NAN status |
Include the following information: Module existence Main interface down/up NAN interface existence |
init |
Init NAN interface Example:
|
Register nan0 interface by this command. iw dev result show Interface nan0, and it share the same phy with wlan0 |
deinit |
deinit NAN interface Example:
|
Un-register nan0 interface by this command. |
start [pref <value>] [bands [2GHz] [5GHz]] |
Start NAN Example:
|
pref:
|
stop |
Stop NAN |
|
add_func type <publish|subscribe|followup> [solicited] [unsolicited] name <name> optional param:
|
Add a NAN function with or without filters Example:
|
Follow up service
Service response filter
Matching filter
|
rm_func <cookie> |
Remove a NAN function with cookie |
Cookie is shown when add func. |
data_req support param:
|
NAN data request Example:
|
|
data_rsp support param:
|
NAN data response Example:
|
|
data_end [ndp_id <id>] [initiator_ndi <mac>] |
NAN data end |
|
set_ipv6 |
Set own ipv6 link-local address based on mac address via ifconfig |
automatically convert own mac address to ipv6 address |
set_neigh <dst_mac> |
Set neighbor ipv6 link-local address with dst mac address |
automatically convert dst mac address to ipv6 address |